CD200Fc reduces LPS-induced IL-1β activation in human cervical cancer cells by modulating TLR4-NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway
- PMID: 28402258
- PMCID: PMC5464862
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16596
CD200Fc reduces LPS-induced IL-1β activation in human cervical cancer cells by modulating TLR4-NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway
Abstract
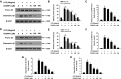
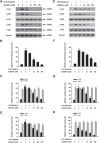
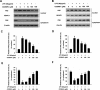
Chronic inflammation plays an important role in tumorigenesis of cervical cancer. CD200Fc, a CD200R1 agonist, has been found to have anti-inflammatory effects in autoimmune diseases and neuro-degeneration. However, the anti-inflammatory effect of CD200Fc on cervical cancer has not yet to be completely understood. This study investigated the anti-inflammatory effects and mechanisms of CD200Fc in LPS-induced human SiHa cells and Caski cells. SiHa cells and Caski cells were stimulated with 40 μg/ml LPS under different concentrations of CD200Fc for 90 min or 12 hours. The mRNA and protein levels of pro-IL-1β, cleaved-IL-1β and NLRP3, as well as the protein level of cleaved caspase-1, were significantly increased in LPS-induced SiHa cells and Caski cells. LPS stimulation did not change ASC and pro-caspase-1 expression. CD200Fc down-regulated protein expression of cleaved caspase-1 and mRNA and protein expression of pro-IL-1β, cleaved-IL-1β and NLRP3. In addition, the protein levels of TLR4, p-P65 and p-IκB, as well as the translocation of P65 to nucleus, were significantly increased in LPS-induced SiHa cells and Caski cells. LPS stimulation did not change t-P65 and t-IκB on protein levels, which were components of TLR-NF-κB pathway. CD200Fc down-regulated protein expression of TLR4, p-P65 and p-IκB and inhibited the translocation of P65 to nucleus in LPS-induced SiHa cells and Caski cells. These results indicated that CD200Fc appeared to suppress the inflammatory activity of TLR4-NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in LPS-induced SiHa cells and Caski cells. It provided novel mechanistic insights into the potential therapeutic uses of CD200Fc for cervical cancer.
Keywords: CD200Fc; IL-1β; NLRP3 inflammasome; TLR4-NF-κB; cervical cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
These authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
CD200Fc reduces TLR4-mediated inflammatory responses in LPS-induced rat primary microglial cells via inhibition of the NF-κB pathway.Inflamm Res. 2016 Jul;65(7):521-32. doi: 10.1007/s00011-016-0932-3. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Inflamm Res. 2016. PMID: 26956766
-
Aloe vera downregulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production and expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages.Mol Immunol. 2013 Dec;56(4):471-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2013.05.005. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23911403
-
Targeting toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and the NLRP3 inflammasome: Novel and emerging therapeutic targets for hyperuricaemia nephropathy.Biomol Biomed. 2023 Dec 1;24(4):688-697. doi: 10.17305/bb.2023.9838. Biomol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 38041694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between ER stress, NLRP3 inflammasome, and inflammation.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jul;104(14):6129-6140. doi: 10.1007/s00253-020-10614-y. Epub 2020 May 24. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32447438 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual Role of Chitin as the Double Edged Sword in Controlling the NLRP3 Inflammasome Driven Gastrointestinal and Gynaecological Tumours.Mar Drugs. 2022 Jul 11;20(7):452. doi: 10.3390/md20070452. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35877745 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NOD-like receptors: major players (and targets) in the interface between innate immunity and cancer.Biosci Rep. 2019 Apr 9;39(4):BSR20181709. doi: 10.1042/BSR20181709. Print 2019 Apr 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30837326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoamine Oxidase-B Inhibitor Reduction in Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Mediated by Inhibition of cAMP-PKA/EPAC Signaling.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 17;12:741460. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.741460. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34867348 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration in gene expression profiles of thymoma: Genetic differences and potential novel targets.Thorac Cancer. 2019 May;10(5):1129-1135. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13053. Epub 2019 Apr 1. Thorac Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30932350 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating the dysregulated inflammasome-based molecular functionome in the malignant transformation of endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 18;9(3):3704-3726. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23364. eCollection 2018 Jan 9. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29423077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Practice Bulletin No. 157: Cervical Cancer Screening and Prevention. Obstetrics and gynecology. 2016;127:e1–e20. - PubMed
-
- Kriek JM, Jaumdally SZ, Masson L, Little F, Mbulawa Z, Gumbi PP, Barnabas SL, Moodley J, Denny L, Coetzee D, Williamson AL, Passmore JA. Female genital tract inflammation, HIV co-infection and persistent mucosal Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infections. Virology. 2016;493:247–254. - PubMed
-
- de Castro-Sobrinho JM, Rabelo-Santos SH, Fugueiredo-Alves RR, Derchain S, Sarian LO, Pitta DR, Campos EA, Zeferino LC. Bacterial vaginosis and inflammatory response showed association with severity of cervical neoplasia in HPV-positive women. Diagnostic cytopathology. 2016;44:80–86. - PubMed
-
- He A, Ji R, Shao J, He C, Jin M, Xu Y. TLR4-MyD88-TRAF6-TAK1 Complex-Mediated NF-kappaB Activation Contribute to the Anti-Inflammatory Effect of V8 in LPS-Induced Human Cervical Cancer SiHa Cells. Inflammation. 2016;39:172–181. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

