Association of CKIP-1 P21A polymorphism with risk of chronic heart failure in a Chinese population
- PMID: 28402261
- PMCID: PMC5482675
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16614
Association of CKIP-1 P21A polymorphism with risk of chronic heart failure in a Chinese population
Abstract
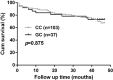
Pathological cardiac hypertrophy is an independent risk factor for chronic heart failure. Casein kinase-2 interacting protein-1 (CKIP-1) can inhibit pathological cardiac hypertrophy. Therefore, we investigated whether CKIP-1 nonsynonymous polymorphism rs2306235 (Pro21Ala) contributes to risk and prognosis of chronic heart failure in a Chinese population.A total of 923 adult patients with chronic heart failure and 1020 age- and gender-matched healthy controls were recruited. CKIP-1 rs2306235 polymorphism was genotyped using PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism. Additional follow-up data for 140 chronic heart failure patients was evaluated. The rs2306235 G allele was associated with an increased risk of chronic heart failure (OR = 1.38, 95% CI = 1.09-1.75, p = 0.007), especially in patients with hypertension (OR = 1.45, 95% CI = 1.09-1.75, p = 0.006) and coronary heart disease (OR = 1.41, 95% CI = 1.09-1.83, p = 0.010) after adjustment for multiple cardiovascular risk factors. However, rs2306235 polymorphism was not associated with cardiovascular mortality in chronic heart failure (p = 0.875). CKIP-1 rs2306235 polymorphism may be a risk factor for chronic heart failure in a Chinese Han population.
Keywords: CKIP-1; cardiac hypertrophy; chronic heart failure; polymorphism; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Associations of CKIP-1 and LOX-1 polymorphisms with the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension among Chinese adults.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Jan;61(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s00592-023-02175-z. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 37668684
-
Basigin rs8259 Polymorphism Confers Decreased Risk of Chronic Heart Failure in a Chinese Population.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Feb 21;14(2):211. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14020211. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28230811 Free PMC article.
-
Association between TNFAIP3 nonsynonymous single-nucleotide polymorphism rs2230926 and chronic hepatitis B virus infection in a Chinese Han population.Virol J. 2015 Feb 28;12:33. doi: 10.1186/s12985-015-0268-6. Virol J. 2015. PMID: 25890346 Free PMC article.
-
The genomic architecture of sporadic heart failure.Circ Res. 2011 May 13;108(10):1270-83. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.229260. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21566223 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical considerations of heritable factors in common heart failure.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2011 Dec;4(6):701-9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.959379. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2011. PMID: 22187448 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Prostatic epithelial cells and their high expressions of CKIP-1 affect the TGF-β1 expression levels which might reduce the scar formation in remodeling stage at prostatic urethral wounds after wound repair.Int Urol Nephrol. 2020 Jan;52(1):97-106. doi: 10.1007/s11255-019-02286-z. Epub 2019 Sep 21. Int Urol Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31542883 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of CKIP-1 and LOX-1 polymorphisms with the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension among Chinese adults.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Jan;61(1):43-52. doi: 10.1007/s00592-023-02175-z. Epub 2023 Sep 5. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 37668684
-
CKIP-1 serves as a negative regulator and correlates with the degree of differentiation in gastric cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017 Oct 1;10(10):10674-10680. eCollection 2017. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2017. PMID: 31966411 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of CKIP-1 inhibits high-glucose induced inflammation and oxidative stress in HRECs and attenuates diabetic retinopathy by modulating Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway: an in vitro study.Cell Biosci. 2019 Aug 23;9:67. doi: 10.1186/s13578-019-0331-x. eCollection 2019. Cell Biosci. 2019. PMID: 31462987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhai YJ, Liu P, He HR, Zheng XW, Wang Y, Yang QT, Dong YL, Lu J. The association of ADORA2A and ADORA2B polymorphisms with the risk and severity of chronic heart failure: a case-control study of a northern Chinese population. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16:2732–46. doi: 10.3390/ijms16022732. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials