Comparing the Efficacy of Drug Regimens for Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Meta-analysis of Endpoints in Early-Phase Clinical Trials
- PMID: 28402396
- PMCID: PMC5850317
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/cix247
Comparing the Efficacy of Drug Regimens for Pulmonary Tuberculosis: Meta-analysis of Endpoints in Early-Phase Clinical Trials
Abstract
Background: A systematic review of early clinical outcomes in tuberculosis was undertaken to determine ranking of efficacy of drugs and combinations, define variability of these measures on different endpoints, and to establish the relationships between them.
Methods: Studies were identified by searching PubMed, Medline, Embase, LILACS (Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature), and reference lists of included studies. Outcomes were early bactericidal activity results over 2, 7, and 14 days, and the proportion of patients with negative culture at 8 weeks.
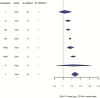
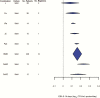
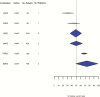
Results: One hundred thirty-three trials reporting phase 2A (early bactericidal activity) and phase 2B (culture conversion at 2 months) outcomes were identified. Only 9 drug combinations were assessed on >1 phase 2A endpoint and only 3 were assessed in both phase 2A and 2B trials.
Conclusions: The existing evidence base supporting phase 2 methodology in tuberculosis is highly incomplete. In future, a broader range of drugs and combinations should be more consistently studied across a greater range of phase 2 endpoints.
Keywords: efficacy; meta-analysis; tuberculosis.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures



Comment in
-
Setting Tuberculosis Regimen Development on a Firm Foundation.Clin Infect Dis. 2017 Jul 1;65(1):55-56. doi: 10.1093/cid/cix250. Clin Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28402531 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lienhardt C, Raviglione M, Spigelman M, et al. New drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis: needs, challenges, promise, and prospects for the future. J Infect Dis 2012; 205(suppl 2):S241–9. - PubMed
-
- Donald PR, Diacon AH. The early bactericidal activity of anti-tuberculosis drugs: a literature review. Tuberculosis (Edinb) 2008; 88(suppl 1):S75–83. - PubMed
-
- Jindani A, Aber VR, Edwards EA, Mitchison DA. The early bactericidal activity of drugs in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Am Rev Respir Dis 1980; 121:939–49. - PubMed
-
- Diacon AH, Dawson R, von Groote-Bidlingmaier F, et al. 14-day bactericidal activity of PA-824, bedaquiline, pyrazinamide, and moxifloxacin combinations: a randomised trial. Lancet 2012; 380:986–93. - PubMed
-
- Rustomjee R, Lienhardt C, Kanyok T, et al. ; Gatifloxacin for TB (OFLOTUB) study team A phase II study of the sterilising activities of ofloxacin, gatifloxacin and moxifloxacin in pulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2008; 12:128–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

