Structure of Nascent Chromatin Is Essential for Hematopoietic Lineage Specification
- PMID: 28402853
- PMCID: PMC5408750
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.03.035
Structure of Nascent Chromatin Is Essential for Hematopoietic Lineage Specification
Abstract
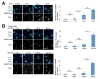
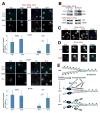
The role of chromatin structure in lineage commitment of multipotent hematopoietic progenitors (HPCs) is presently unclear. We show here that CD34+ HPCs possess a post-replicative chromatin globally devoid of the repressive histone mark H3K27me3. This H3K27-unmodified chromatin is required for recruitment of lineage-determining transcription factors (TFs) C/EBPα, PU.1, and GATA-1 to DNA just after DNA replication upon cytokine-induced myeloid or erythroid commitment. Blocking DNA replication or increasing H3K27me3 levels prevents recruitment of these TFs to DNA and suppresses cytokine-induced erythroid or myeloid differentiation. However, H3K27me3 is rapidly associated with nascent DNA in more primitive human and murine HPCs. Treatment of these cells with instructive cytokines leads to a significant delay in accumulation of H3K27me3 in nascent chromatin due to activity of the H3K27me3 demethylase UTX. Thus, HPCs utilize special mechanisms of chromatin modification for recruitment of specific TFs to DNA during early stages of lineage specification.
Keywords: DNA replication; H3K27me3; HMTs; KDMs; hematopoietic progenitors; myeloid and erythroid differentiation; nascent DNA; nascent chromatin; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Bell O, Schwaiger M, Oakeley EJ, Lienert F, Beisel C, Stadler MB, Schubeler D. Accessibility of the Drosophila genome discriminates PcG repression, H4K16 acetylation and replication timing. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2010;17:894–900. - PubMed
-
- Cantor AB, Orkin SH. Hematopoietic development: a balancing act. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2001;11:513–519. - PubMed
-
- Dahl R, Walsh JC, Lancki D, Laslo P, Iyer SR, Singh H, Simon MC. Regulation of macrophage and neutrophil cell fates by the PU.1:C/EBPalpha ratio and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:1029–1036. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

