Mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 expression and prognostic relevance in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a summary of immunohistochemical studies
- PMID: 28402953
- PMCID: PMC5546533
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16680
Mechanisms of PD-1/PD-L1 expression and prognostic relevance in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a summary of immunohistochemical studies
Abstract
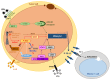
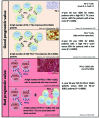
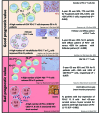
Immune checkpoint blockade therapeutics, notably antibodies targeting the programmed death 1 (PD-1) receptor and its PD-L1 and PD-L2 ligands, are currently revolutionizing the treatment of cancer. For a sizeable fraction of patients with melanoma, lung, kidney and several other solid cancers, monoclonal antibodies that neutralize the interactions of the PD-1/PD-L1 complex allow the reconstitution of long-lasting antitumor immunity. In hematological malignancies this novel therapeutic strategy is far less documented, although promising clinical responses have been seen in refractory and relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma patients. This review describes our current knowledge of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression, as reported by immunohistochemical staining in both non-Hodgkin lymphoma cells and their surrounding immune cells. Here, we discuss the multiple intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms by which both T and B cell lymphomas up-regulate the PD-1/PD-L1 axis, and review current knowledge about the prognostic significance of its immunohistochemical detection. This body of literature establishes the cell surface expression of PD-1/PD-L1 as a critical determinant for the identification of non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients eligible for immune checkpoint blockade therapies.
Keywords: PD-1/PD-L1 expression; non-Hodgkin lymphoma; prognostic value.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Challa-Malladi M, Lieu YK, Califano O, Holmes AB, Bhagat G, Murty VV, Dominguez-Sola D, Pasqualucci L, Dalla-Favera R. Combined genetic inactivation of β2-Microglobulin and CD58 reveals frequent escape from immune recognition in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:728–40. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Green MR, Kihira S, Liu CL, Nair RV, Salari R, Gentles AJ, Irish J, Stehr H, Vicente-Dueñas C, Romero-Camarero I, Sanchez-Garcia I, Plevritis SK, Arber DA, et al. Mutations in early follicular lymphoma progenitors are associated with suppressed antigen presentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112:E1116–25. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Béguelin W, Sawh S, Chambwe N, Chan FC, Jiang Y, Choo JW, Scott DW, Chalmers A, Geng H, Tsikitas L, Tam W, Bhagat G, Gascoyne RD, Shaknovich R. IL10 receptor is a novel therapeutic target in DLBCLs. Leukemia. 2015;29:1684–94. - PubMed
-
- Amé-Thomas P, Tarte K. The yin and the yang of follicular lymphoma cell niches: role of microenvironment heterogeneity and plasticity. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014;24:23–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

