Reference interval for the disc-macula distance to disc diameter ratio in a large population of healthy Japanese adults: A prospective, observational study
- PMID: 28403107
- PMCID: PMC5403104
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006613
Reference interval for the disc-macula distance to disc diameter ratio in a large population of healthy Japanese adults: A prospective, observational study
Abstract
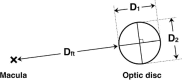
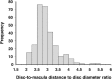
This study presents the calculated reference interval for the disc-to-macula distance to disc diameter ratio (DM:DD) based on a large population of healthy Japanese adults.A total of 308 consecutive, healthy Japanese adults were examined in this prospective observational study. Eighteen subjects were also excluded because of poor quality of the fundus photograph of one or both eyes; 290 (161 men and 129 women) were included in this study. For each subject, a color fundus photograph of one eye, either the right or left, was randomly selected and used for analysis. On the photograph, the distances between the fovea and the nearest temporal margin of the optic disc (Dft), and the two kinds of disc diameters (D1 and D2), which bisected at right angles and one of which was directed to the fovea (D1), were measured. DM:DD was estimated using the formula: (2Dft + D1)/(D1 + D2).The mean ± standard deviation of DM:DD was 2.91 ± 0.49 for men and 2.96 ± 0.54 for women; there was no sex difference (P = .78, Mann-Whitney U test). Also, almost no relationship was found between DM:DD and age (ρ = -.12, P = .04, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient). The data did not fit a normal distribution (P < .001, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). The estimated reference interval for DM:DD corresponding to the 2.5th and 97.5th percentiles was 2.12 to 4.18.Using a nonparametric approach, the reference interval for DM:DD of a large population of healthy Japanese adults was calculated to be 2.12 to 4.18, regardless of age or sex.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An appraisal of the disc-macula distance to disc diameter ratio in the assessment of optic disc size.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1999 Sep;19(5):365-75. doi: 10.1046/j.1475-1313.1999.00463.x. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 1999. PMID: 10768018
-
A simple clinical method of assessing patients with optic nerve hypoplasia. The disc-macula distance to disc diameter ratio (DM/DD).Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1987 Oct;65(5):612-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.1987.tb07051.x. Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh). 1987. PMID: 3425270
-
Comparison of Heidelberg Retina Tomograph with disc-macula distance to disc diameter ratio in diagnosing optic nerve hypoplasia.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2016 May;36(3):317-23. doi: 10.1111/opo.12274. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2016. PMID: 26799143
-
[A new approach for studying the retinal and choroidal circulation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):836-61; discussion 862. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656089 Review. Japanese.
-
The morphology of the optic nerve head in the Singaporean Chinese population (the Tanjong Pagar study): part 1--Optic nerve head morphology.Br J Ophthalmol. 2008 Mar;92(3):303-9. doi: 10.1136/bjo.2007.123273. Br J Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18303151 Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormalities of the Optic Nerve in Down Syndrome and Associations With Visual Acuity.Front Neurol. 2019 Jun 14;10:633. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00633. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31258511 Free PMC article.
-
Color Vision in Aniridia.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Apr 1;59(5):2142-2152. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-23047. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29801149 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burk RO, Rohrschneidern K, Noack H, et al. Are large optic nerve heads susceptible to glaucomatous damage at normal intraocular pressure? A three dimensional study by laser scanning tomography. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 1992;230:552–60. - PubMed
-
- Awan KJ. Ganglionic neuroretinal aplasia and hypoplasia: aplasia and hypoplasia of optic nerve. Ann Ophthalmol 1976;8:1193–202. - PubMed
-
- Wakakura M, Alvarez E. A simple clinical method of assessing patients with optic nerve hypoplasia. The disc-macula distance to disc diameter ratio (DM/DD). Acta Ophthalmol (Copenh) 1987;65:612–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

