Analogosedation during flexible bronchoscopy using a combination of midazolam, propofol and fentanyl - A retrospective analysis
- PMID: 28403208
- PMCID: PMC5389664
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175394
Analogosedation during flexible bronchoscopy using a combination of midazolam, propofol and fentanyl - A retrospective analysis
Abstract
Background: According to current guidelines flexible bronchoscopy is usually performed under sedation. Previously it has been demonstrated that combined sedation with e. g. the combination of midazolam and propofol or an opioid might have several advantages over sedation with just one sedative drug. However, little is known about the efficacy and safety of combined sedation with midazolam, fentanyl and propofol (MFP) compared to sedation with midazolam and fentanyl (MF) or midazolam and propofol (MP).
Methods: We carried out a retrospective analysis of bronchoscopies performed under triple (MFP) or double sedation (MF and MP) in an academic hospital. 1392 procedures were analyzed (MFP: n = 824; MF: n = 272; MP: n = 296). In particular, we compared the occurrence of complications and the dosage of administered sedative drugs between the groups.
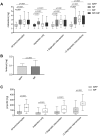
Results: The occurrence of adverse events (MFP vs. MF: odds ratio (OR) 1.116 [95% CI 0.7741 to 1.604]; MFP vs. MP: OR 0.8296 [95% CI 0.5939 to 1.16] and severe adverse events (MFP vs. MF: OR 1.581 [95% CI 0.5594 to 4.336]; MFP vs. MP: OR 3.47 [95% CI 0.908 to 15.15]; all p>0.05) was similar in all groups. The dosage of midazolam was lower in the MFP compared to the MF or MP group (MFP vs. MF: Cohen's d 0.075; MFP vs. MP: Cohen's d 0.225; all p<0.001). In addition patients in the MFP group received significantly less propofol compared to the MP group (Cohen's d 1.22; p<0.001).
Conclusions: In summary we were able to demonstrate that triple sedation can safely be administered during flexible bronchoscopy and is associated with a reduced dosage of midazolam and propofol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Du Rand IA, Barber P V, Goldring J, Lewis RA, Mandal S, Munavvar M, et al. British Thoracic Society guideline for advanced diagnostic and therapeutic flexible bronchoscopy in adults. Thorax. 2011;66 Suppl 3: iii1–21. - PubMed
-
- Stolz D, Kurer G, Meyer a, Chhajed PN, Pflimlin E, Strobel W, et al. Propofol versus combined sedation in flexible bronchoscopy: a randomised non-inferiority trial. Eur Respir J Off J Eur Soc Clin Respir Physiol. 2009;34: 1024–1030. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

