Health workers perceptions and attitude about Ghana's preparedness towards preventing, containing, and managing Ebola Virus Disease
- PMID: 28403852
- PMCID: PMC5389014
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-017-2225-0
Health workers perceptions and attitude about Ghana's preparedness towards preventing, containing, and managing Ebola Virus Disease
Abstract
Background: Ebola virus is highly infectious and the disease can be very fatal. The World Health Organization has declared the 2014-2015 Ebola Virus Disease outbreak a Public Health Emergency of International Concern. In response to this, preparations were made in various health facilities and entry points across Ghana. This study explored health workers perceptions, and attitude about Ghana's preparedness towards preventing and containing Ebola Virus Disease.
Methods: We conducted a qualitative study in five (5) of the ten (10) regions in Ghana. Five focus group discussions (N = 44) were conducted among nurses; one in each region. In addition, ten (10) health workers (2 in each region) who are members of regional Ebola Virus Disease task force were recruited and interviewed. In the Greater Accra, Volta and Western regions that have ports, six (6) port health officials: two in each of these regions were also interviewed. The interviews were recorded digitally and transcribed verbatim. Thematic content analysis was used to analyze the transcripts with the aid of NVivo 10 software.
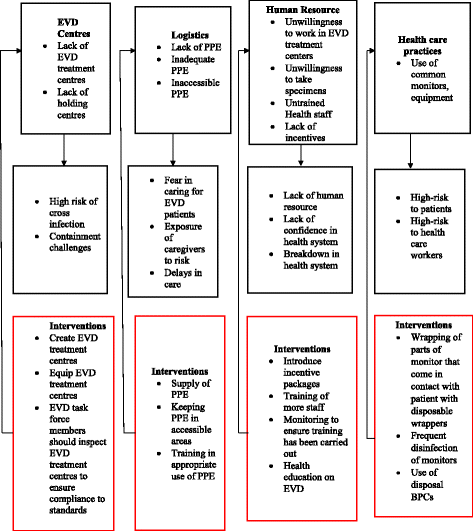
Results: The results of this study showed that Ghanaian health workers perceived the screening at various ports as important and ongoing but felt that the screenings at in-land ports were being undermined by the use of unapproved routes. Training of health workers was also being carried out in all the regions, however, there was a general perception among 33 out of 44 nurses that majority of health workers have not received training on Ebola Virus Disease prevention and management. Logistical challenges were also reported as some health facilities did not have adequate Personal Protective Equipment. In facilities where equipment was available, they were stored in places which are not easily accessible to health workers at all times of the day. Human resource preparation was also perceived to be a challenge as health workers (38/44 of nurses) generally expressed fear and unwillingness to work in Ebola treatment centres in the event of an outbreak in Ghana.
Conclusions: Our study concludes that preparatory work for Ebola Virus Disease prevention and containment in Ghana is perceived as inadequate by health workers. Ghana needs to strengthen preparation in the area of training of health workers, provision and accessibility of Personal Protective Equipment and incentives for health workers to better position her to contain and manage any Ebola Virus Disease outbreak.
Keywords: Ebola Virus Disease; Ghana; Health System; Health Workers; Perception; Preparedness.
Figures
References
-
- Rio C, Mehta AK, Marshall Lyon MG, Guarner J. Ideas and Opinions Annals of Internal Medicine Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever in 2014 : The Tale of an Evolving Epidemic. Ann Intern Med. 2014;6(10):746–749. - PubMed
-
- WHO: Ebola Virus Disease in Guinea – Update. Geneva: World Health Organisation; 2014.
-
- Statement on the 1st meeting of the IHR Emergency Committee on the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa [http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/statements/2014/ebola-20140808/en/]. Accessed 28 Nov 2015.
-
- Ebola Situation Reports [http://apps.who.int/ebola/ebola-situation-reports]. Accessed 28 Nov 2015.
-
- UNDG – Western and Central Africa: Socio-Economic Impact of Ebola Virus Disease in West African Countries A Call for National and Regional Containment, Recovery and Prevention. Western and Central Africa; 2015.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical