A systematic tale of two differing reviews: evaluating the evidence on public and private sector quality of primary care in low and middle income countries
- PMID: 28403871
- PMCID: PMC5389193
- DOI: 10.1186/s12992-017-0246-4
A systematic tale of two differing reviews: evaluating the evidence on public and private sector quality of primary care in low and middle income countries
Abstract
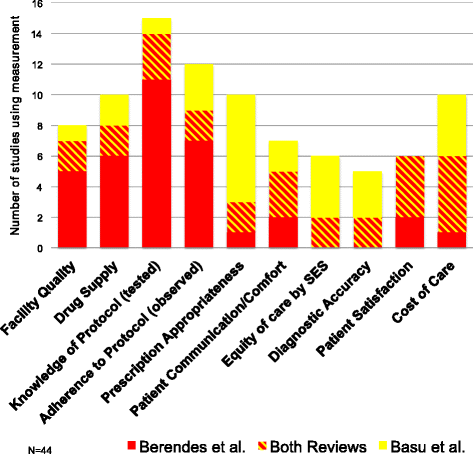
Systematic reviews are powerful tools for summarizing vast amounts of data in controversial areas; but their utility is limited by methodological choices and assumptions. Two systematic reviews of literature on the quality of private sector primary care in low and middle income countries (LMIC), published in the same journal within a year, reached conflicting conclusions. The difference in findings reflects different review methodologies, but more importantly, a weak underlying body of literature. A detailed examination of the literature cited in both reviews shows that only one of the underlying studies met the gold standard for methodological robustness. Given the current policy momentum on universal health coverage and primary health care reform across the globe, there is an urgent need for high quality empirical evidence on the quality of private versus public sector primary health care in LMIC.
Keywords: LMIC; Primary Care; Primary Health Care; Public versus Private care; Quality of Care; Systematic Reviews.
Figures
References
-
- Assembly UNG . Agenda item 123. Global health and foriegn policy, a/67/L36. In: Aseembly UNG, editor. New York. New York: United Nations; 2012.
-
- Wagstaff A. Universal Health Coverage: Old wine in a new bottle? If so, is that so bad? Lets Talk Development: World Bank. 2013. Available at http://blogs.worldbank.org/developmenttalk/universal-health-coverage-old.... Accessed 30 June 2014.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous