Global analysis of H3K27me3 as an epigenetic marker in prostate cancer progression
- PMID: 28403887
- PMCID: PMC5388998
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3256-y
Global analysis of H3K27me3 as an epigenetic marker in prostate cancer progression
Abstract
Background: H3K27me3 histone marks shape the inhibition of gene transcription. In prostate cancer, the deregulation of H3K27me3 marks might play a role in prostate tumor progression.
Methods: We investigated genome-wide H3K27me3 histone methylation profile using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and 2X400K promoter microarrays to identify differentially-enriched regions in biopsy samples from prostate cancer patients. H3K27me3 marks were assessed in 34 prostate tumors: 11 with Gleason score > 7 (GS > 7), 10 with Gleason score ≤ 7 (GS ≤ 7), and 13 morphologically normal prostate samples.
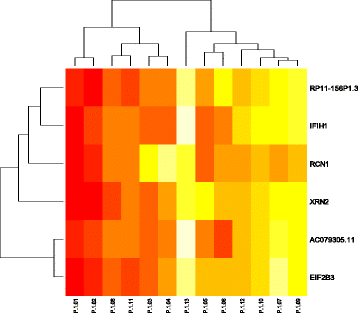
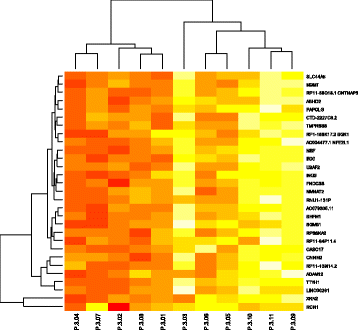
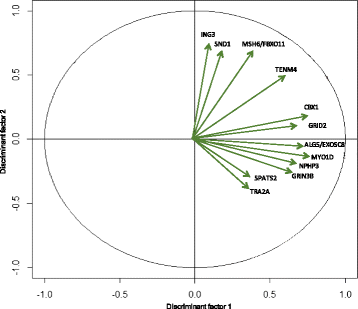
Results: Here, H3K27me3 profiling identified an average of 386 enriched-genes on promoter regions in healthy control group versus 545 genes in GS ≤ 7 and 748 genes in GS > 7 group. We then ran a factorial discriminant analysis (FDA) and compared the enriched genes in prostate-tumor biopsies and normal biopsies using ANOVA to identify significantly differentially-enriched genes. The analysis identified ALG5, EXOSC8, CBX1, GRID2, GRIN3B, ING3, MYO1D, NPHP3-AS1, MSH6, FBXO11, SND1, SPATS2, TENM4 and TRA2A genes. These genes are possibly associated with prostate cancer. Notably, the H3K27me3 histone mark emerged as a novel regulatory mechanism in poor-prognosis prostate cancer.
Conclusions: Our findings point to epigenetic mark H3K27me3 as an important event in prostate carcinogenesis and progression. The results reported here provide new molecular insights into the pathogenesis of prostate cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; ChIP-on-chip; Epigenetics; H3K27me3; Histone methylation; Prostate.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

