Diagnosis and management of psoriasis
- PMID: 28404701
- PMCID: PMC5389757
Diagnosis and management of psoriasis
Abstract
Objective: To provide primary care clinicians with an up-to-date and practical overview of the diagnosis and management of psoriasis.
Quality of evidence: PubMed, MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases were searched for relevant meta-analyses, randomized controlled trials, systematic reviews, and observational studies about the diagnosis and management of psoriasis.
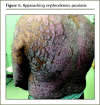
Main message: Psoriasis is a chronic, multisystem inflammatory disease with predominantly skin and joint involvement. Beyond the physical dimensions of disease, psoriasis has an extensive emotional and psychosocial effect on patients, affecting social functioning and interpersonal relationships. As a disease of systemic inflammation, psoriasis is associated with multiple comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease and malignancy. The diagnosis is primarily clinical and a skin biopsy is seldom required. Depending on the severity of disease, appropriate treatment can be initiated. For mild to moderate disease, first-line treatment involves topical therapies including corticosteroids, vitamin D3 analogues, and combination products. These topical treatments are efficacious and can be safely initiated and prescribed by primary care physicians. Patients with more severe and refractory symptoms might require further evaluation by a dermatologist for systemic therapy.
Conclusion: Many patients with psoriasis seek initial evaluation and treatment from their primary care providers. Recognition of psoriasis, as well as its associated medical and psychiatric comorbidities, would facilitate timely diagnosis and appropriate management with effective and safe topical therapies and other medical and psychological interventions, as needed. More severe and refractory cases might warrant referral to a dermatologist for further evaluation and possible systemic therapy.
Copyright© the College of Family Physicians of Canada.
Figures


References
-
- Canadian Psoriasis Guidelines Committee. Canadian guidelines for the management of plaque psoriasis. Ottawa, ON: Canadian Dermatology Association; 2009.
-
- Griffiths CE, Barker JN. Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet. 2007;370(9583):263–71. - PubMed
-
- Levine D, Gottlieb A. Evaluation and management of psoriasis: an internist’s guide. Med Clin North Am. 2009;93(6):1291–303. - PubMed
-
- Menter A, Gottlieb A, Feldman SR, Van Voorhees AS, Leonardi CL, Gordon KB, et al. Guidelines of care for the management of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: section 1. Overview of psoriasis and guidelines of care for the treatment of psoriasis with biologics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58(5):826–50. - PubMed
-
- Feldman SR, Fleischer AB, Jr, Cooper JZ. New topical treatments change the pattern of treatment of psoriasis: dermatologists remain the primary providers of this care. Int J Dermatol. 2000;39(1):41–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
