Toxoplasma Effectors Targeting Host Signaling and Transcription
- PMID: 28404792
- PMCID: PMC5475222
- DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00005-17
Toxoplasma Effectors Targeting Host Signaling and Transcription
Abstract
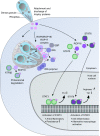
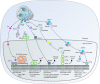
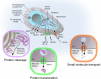
Early electron microscopy studies revealed the elaborate cellular features that define the unique adaptations of apicomplexan parasites. Among these were bulbous rhoptry (ROP) organelles and small, dense granules (GRAs), both of which are secreted during invasion of host cells. These early morphological studies were followed by the exploration of the cellular contents of these secretory organelles, revealing them to be comprised of highly divergent protein families with few conserved domains or predicted functions. In parallel, studies on host-pathogen interactions identified many host signaling pathways that were mysteriously altered by infection. It was only with the advent of forward and reverse genetic strategies that the connections between individual parasite effectors and the specific host pathways that they targeted finally became clear. The current repertoire of parasite effectors includes ROP kinases and pseudokinases that are secreted during invasion and that block host immune pathways. Similarly, many secretory GRA proteins alter host gene expression by activating host transcription factors, through modification of chromatin, or by inducing small noncoding RNAs. These effectors highlight novel mechanisms by which T. gondii has learned to harness host signaling to favor intracellular survival and will guide future studies designed to uncover the additional complexity of this intricate host-pathogen interaction.
Keywords: chromatin remodeling; epigenetics; immune evasion; innate immunity; intracellular pathogen; serine/threonine kinases; signal transduction; transcription factors.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Dubey JP. 2010. Toxoplasmosis of animals and humans. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
-
- Levine ND. 1988. The protozoan phylum Apicomplexa, vol 1 and 2. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
-
- Pawlowski J, Audic S, Adl S, Bass D, Belbahri L, Berney C, Bowser SS, Cepicka I, Decelle J, Dunthorn M, Fiore-Donno AM, Gile GH, Holzmann M, Jahn R, Jirku M, Keeling PJ, Kostka M, Kudryavtsev A, Lara E, Lukes J, Mann DG, Mitchell EA, Nitsche F, Romeralo M, Saunders GW, Simpson AG, Smirnov AV, Spouge JL, Stern RF, Stoeck T, Zimmermann J, Schindel D, de Vargas C. 2012. CBOL protist working group: barcoding eukaryotic richness beyond the animal, plant, and fungal kingdoms. PLoS Biol 10:e1001419. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.1001419. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

