Flattened microvessel independently predicts poor prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 28404911
- PMCID: PMC5444728
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15617
Flattened microvessel independently predicts poor prognosis of patients with non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
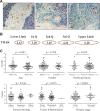
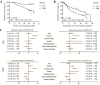
Angiogenesis plays an essential role in improving tumor progression, whereas, its value in prognosis predicting remains controversial, especially in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Most recently, microvessel pattern has been raised as a novel prognosis factor. In this study, flattened microvessel, evaluated by tumor microvessel aspect ratio (TMAR), was conducted as a prognostic factor in NSCLC patients. A total of 100 patients with NSCLC were retrospectively reviewed. Microvessel in tumor was visualized by immunochemistry staining and then TMAR was determined. The prognostic role of TMAR was evaluated by univariate and multivariate analysis. Most of intratumor microvessels were flattened with a median TMAR of 3.65 (range, 2.43 - 6.28). Patients were stratified into high TMAR group (TMAR ≥ 3.6) and low TMAR group (TMAR < 3.6). Compared with subpopulation with low TMAR, high TMAR had significantly high risk of cancer-related death (univariate analysis: HR = 5.06, 95% CI: 2.44-10.47, p<0.001; multivariate analysis: HR = 4.53, 95% CI: 1.70-12.06, p=0.002).In conclusion, the results of our study demonstrate that flattened microvessel in tumor tissue is a promising prognosis predictor of NSCLC patients.
Keywords: aspect ratio; flattened microvessel; microvessel abnormality; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Reck M, Heigener DF, Mok T, Soria JC, Rabe KF. Management of non-small-cell lung cancer: Recent developments. Lancet. 2013;382:709–19. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74. - PubMed
-
- Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature. 2005;438:932–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

