Acanthopanax senticosus polysaccharides-induced intestinal tight junction injury alleviation via inhibition of NF-κB/MLCK pathway in a mouse endotoxemia model
- PMID: 28405145
- PMCID: PMC5374129
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i12.2175
Acanthopanax senticosus polysaccharides-induced intestinal tight junction injury alleviation via inhibition of NF-κB/MLCK pathway in a mouse endotoxemia model
Abstract
Aim: To examine the effects of Acanthopanax senticosus polysaccharides (ASPS) on intestinal tight junction (TJ) disruption and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB)/myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) activation in endotoxemia.
Methods: BALB/C mice (6-8-weeks-old) received continuous intragastric gavage of ASPS for 7 d before injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), or received ASPS once after LPS injection. Blood and intestinal mucosal samples were collected 6 h after LPS challenge. Clinical symptoms, histological injury, intestinal permeability, TJ ultrastructure, and TJ protein expression were determined.
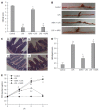
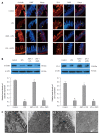
Results: Compared with mice in the LPS group, pretreatment with ASPS improved clinical and histological scores by 390.9% (P < 0.05) and 57.89% (P < 0.05), respectively, and gut permeability change in endotoxemic mice was shown by a 61.93% reduction in reduced leakage of fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran 6 h after LPS injection (P < 0.05). ASPS pretreatment also prevented LPS-induced TJ ultrastructure breakdown supported by increased electron dense materials between adjoining cells, sustained redistribution and expression of occludin (0.597 ± 0.027 vs 0.103 ± 0.009, P < 0.05) and zonula occludens-1 (0.507 ± 0.032 vs 0.125 ± 0.019, P < 0.05), and suppressed activation of the NF-κB/MLCK pathway indicated by reduced expression of NF-κB, phospho-inhibitor kappa B-alpha, MLCK and phospho-myosin light-chain-2 by 16.06% (P < 0.05), 54.31% (P < 0.05), 66.10% (P < 0.05) and 64.82% (P < 0.05), respectively.
Conclusion: ASPS pretreatment may be associated with inhibition of the NF-κB/MLCK pathway and concomitant amelioration of LPS-induced TJ dysfunction of intestinal epithelium in endotoxemia.
Keywords: Acanthopanax senticosus polysaccharide; Intestinal permeability; Myosin light chain kinase; Nuclear factor-kappa B; Tight junction.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this study.
Figures

References
-
- Angus DC, Wax RS. Epidemiology of sepsis: an update. Crit Care Med. 2001;29:S109–S116. - PubMed
-
- Polderman KH, Girbes AR. Drug intervention trials in sepsis: divergent results. Lancet. 2004;363:1721–1723. - PubMed
-
- Hassoun HT, Kone BC, Mercer DW, Moody FG, Weisbrodt NW, Moore FA. Post-injury multiple organ failure: the role of the gut. Shock. 2001;15:1–10. - PubMed
-
- De-Souza DA, Greene LJ. Intestinal permeability and systemic infections in critically ill patients: effect of glutamine. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:1125–1135. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

