Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-3 (MKP-3) in the surgical wound is necessary for the resolution of postoperative pain in mice
- PMID: 28405172
- PMCID: PMC5378457
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S129826
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-3 (MKP-3) in the surgical wound is necessary for the resolution of postoperative pain in mice
Abstract
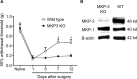
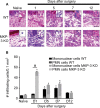
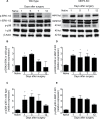
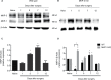
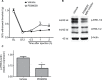
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase-3 (MKP-3) and its substrates (extracellular signal-regulated kinase [ERK] and p38) play an important role in pathophysiological mechanisms of acute postoperative and chronic neuropathic pain in the spinal cord. This study aimed to understand the role of MKP-3 and its target MAPKs at the site of surgical incision in nociceptive behavior. Wild-type (WT) and MKP-3 knockout (KO) mice underwent unilateral plantar hind paw incision. Mechanical allodynia was assessed by using von Frey filaments. Peripheral ERK-1/2 and p38 phosphorylation were measured by Western blot. Cell infiltration was determined using hematoxylin and eosin histological staining. Peripheral phosphorylated ERK-1/2 (p-ERK-1/2) inhibition was performed in MKP-3 KO mice. In WT mice, mechanical hypersensitivity was observed on postoperative day 1 (0.69±0.17 g baseline vs 0.13±0.08 g day 1), which resolved normally by postoperative day 12 (0.46±0.08 g, N=6). In MKP-3 KO mice, this hypersensitivity persisted at least 12 days after surgery (0.19±0.06 g; N=6). KO mice displayed higher numbers of infiltrating cells (51.4±6 cells/0.1 mm2) than WT mice (8.7±1.2 cells/0.1 mm2) on postoperative day 1 (vs 5-6 cells/0.1 mm2 at baseline) that returned to baseline 12 days after surgery (10-12 cells/0.1 mm2). In WT mice, peripheral p-p38 and p-ERK-1/2 expression increased (5- and 3-fold, respectively) on postoperative days 1 and 5, and returned to basal levels 7-12 days after surgery (N=3 per group). Peripheral p-p38 levels in MKP-3 KO mice followed a similar expression pattern as WT mice. Peripheral p-ERK-1/2 levels in MKP-3 KO mice remained elevated 12 days after surgery (2.5-fold, N=3 per group). Administration of PD98059 (MEK inhibitor, N=8, vehicle N=9) reduced p-ERK-1/2 expression in the incised tissue and blocked hypersensitivity in MKP-3 KO mice (N=6). The findings of this study suggest that MKP-3 is pivotal for normal resolution of acute postoperative allodynia, through the regulation of peripheral p-ERK-1/2.
Keywords: DUSP-6; ERK; p38.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Macrae WA. Chronic post-surgical pain: 10 years on. Br J Anaesth. 2008;101(1):77–86. - PubMed
-
- Wu CL, Raja SN. Treatment of acute postoperative pain. Lancet. 25. 2011;377(9784):2215–2225. - PubMed
-
- Wen YR, Suter MR, Ji RR, et al. Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in spinal microglia contributes to incision-induced mechanical allodynia. Anesthesiology. 2009;110(1):155–165. - PubMed
-
- Tong SE, Daniels SE, Black P, Chang S, Protter A, Desjardins PJ. Novel p38alpha mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor shows analgesic efficacy in acute postsurgical dental pain. J Clin Pharmacol. 2012;52(5):717–728. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

