Compound 19e, a Novel Glucokinase Activator, Protects against Cytokine-Induced Beta-Cell Apoptosis in INS-1 Cells
- PMID: 28405188
- PMCID: PMC5370240
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00169
Compound 19e, a Novel Glucokinase Activator, Protects against Cytokine-Induced Beta-Cell Apoptosis in INS-1 Cells
Abstract
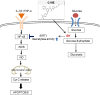
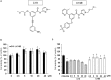
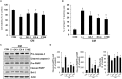
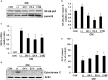
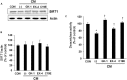
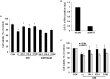
Previously, compound 19e, a novel heteroaryl-containing benzamide derivative, was identified as a potent glucokinase activator (GKA) and showed a glucose-lowering effect in diabetic mice. In this study, the anti-apoptotic actions of 19e were evaluated in INS-1 pancreatic beta-cells co-treated with TNF-α and IL-1β to induce cell death. Compound 19e protected INS-1 cells from cytokine-induced cell death, and the effect was similar to treatment with another GKA or exendin-4. Compound 19e reduced annexin-V stained cells and the expression of cleaved caspase-3 and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase protein, as well as upregulated the expression of B-cell lymphoma-2 protein. Compound 19e inhibited apoptotic signaling via induction of the ATP content, and the effect was correlated with the downregulation of nuclear factor-κB p65 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Further, 19e increased NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) deacetylase activity, and the anti-apoptotic effect of 19e was attenuated by SIRT1 inhibitor or SIRT1 siRNA treatment. Our results demonstrate that the novel GKA, 19e, prevents cytokine-induced beta-cell apoptosis via SIRT1 activation and has potential as a therapeutic drug for the preservation of pancreatic beta-cells.
Keywords: NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin -1; apoptosis; beta-cell; compound 19e; cytokine; glucokinase activator.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment with glucokinase activator, YH-GKA, increases cell proliferation and decreases glucotoxic apoptosis in INS-1 cells.Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014 Jan 23;51:137-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ejps.2013.09.005. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2014. PMID: 24056026
-
Discovery of 3-(4-methanesulfonylphenoxy)-N-[1-(2-methoxy-ethoxymethyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl]-5-(3-methylpyridin-2-yl)-benzamide as a novel glucokinase activator (GKA) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 Apr 1;22(7):2280-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.02.009. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24588963
-
Artesunate protects pancreatic beta cells against cytokine-induced damage via SIRT1 inhibiting NF-κB activation.J Endocrinol Invest. 2016 Jan;39(1):83-91. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0328-1. Epub 2015 Jun 11. J Endocrinol Invest. 2016. PMID: 26062521
-
Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):1939-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770291 Review.
-
Identification of YH-GKA, a novel benzamide glucokinase activator as therapeutic candidate for type 2 diabetes mellitus.Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Dec;35(12):2029-33. doi: 10.1007/s12272-012-1201-9. Arch Pharm Res. 2012. PMID: 23263798 Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuins as Key Regulators in Pancreatic Cancer: Insights into Signaling Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 6;16(23):4095. doi: 10.3390/cancers16234095. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B Cell Lymphoma 2: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10442. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910442. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulation of caveolin-1 and its colocalization with cytokine receptors contributes to beta cell apoptosis.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 14;9(1):16785. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53278-z. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31728004 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of HDACs: Pathology and Therapeutic Targets in Diabetes Mellitus.Cells. 2021 May 28;10(6):1340. doi: 10.3390/cells10061340. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34071497 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bonadonna R. C., Heise T., Arbet-Engels C., Kapitza C., Avogaro A., Grimsby J., et al. (2010). Piragliatin (RO4389620), a novel glucokinase activator, lowers plasma glucose both in the postabsorptive state and after a glucose challenge in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a mechanistic study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95 5028–5036. 10.1210/jc.2010-1041 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

