Modulation of benzo[a]pyrene-DNA adduct formation by CYP1 inducer and inhibitor
- PMID: 28405246
- PMCID: PMC5385587
- DOI: 10.1186/s41021-017-0076-x
Modulation of benzo[a]pyrene-DNA adduct formation by CYP1 inducer and inhibitor
Abstract
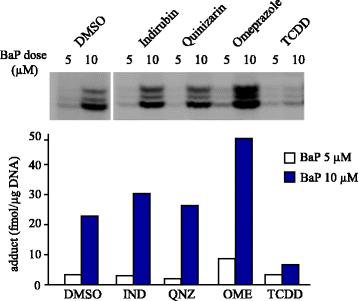
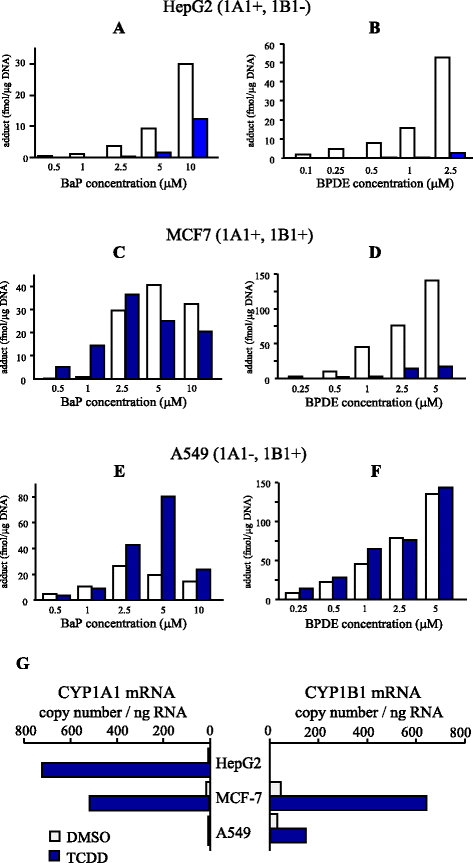
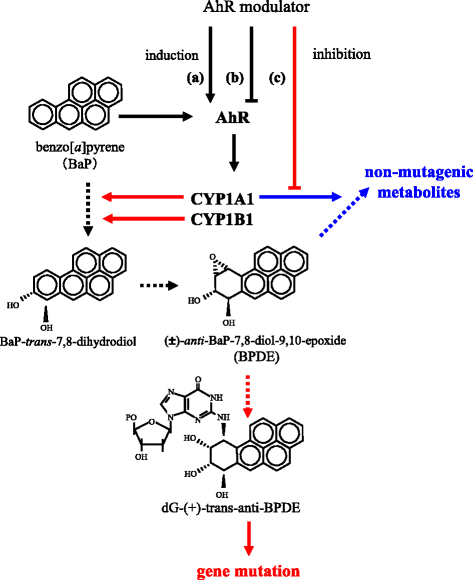
Benzo[a]pyrene (BaP) is a well-studied pro-carcinogen that is metabolically activated by cytochrome P450 enzymes. Cytochrome P4501A1 (CYP1A1) has been considered to play a central role in the activation step, which is essential for the formation of DNA adducts. This enzyme is strongly induced by many different chemical agents, including 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), which binds to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). Therefore, AhR activators are suspected to have the potential to aggravate the toxicity of BaP through the induction of CYP1A1. Besides, CYP1A1 inhibitors, including its substrates, are estimated to have preventive effects against BaP toxicity. However, strangely, increased hepatic BaP-DNA adduct levels have been reported in Cyp1a1 knockout mice. Moreover, numerous reports describe that concomitant treatment of AhR activators reduced BaP-DNA adduct formation. In an experiment using several human cell lines, TCDD had diverse modulatory effects on BaP-DNA adducts, both enhancing and inhibiting their formation. In this review, we focus on the factors that could influence the BaP-DNA adduct formation. To interpret these complicated outcomes, we propose a hypothesis that CYP1A1 is a key enzyme for both generation and reduction of (±)-anti-benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-diol-9,10-epoxide (BPDE), the major carcinogenic intermediate of BaP. Conversely, CYP1B1 is thought to contribute only to the metabolic activation of BaP related to carcinogenesis.
Keywords: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor; Benzo[a]pyrene; Cytochrome P450; DNA adduct.
Figures
References
-
- Gelboin HV. Benzo[a]pyrene metabolism activation and carcinogenesis: role and regulation of mixed-function oxidases and related enzymes. Physiol Rev. 1980;60:1107–1166. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

