M1-like monocytes are a major immunological determinant of severity in previously healthy adults with life-threatening influenza
- PMID: 28405622
- PMCID: PMC5374077
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.91868
M1-like monocytes are a major immunological determinant of severity in previously healthy adults with life-threatening influenza
Abstract
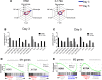
In each influenza season, a distinct group of young, otherwise healthy individuals with no risk factors succumbs to life-threatening infection. To better understand the cause for this, we analyzed a broad range of immune responses in blood from a unique cohort of patients, comprising previously healthy individuals hospitalized with and without respiratory failure during one influenza season, and infected with one specific influenza A strain. This analysis was compared with similarly hospitalized influenza patients with known risk factors (total of n = 60 patients recruited). We found a sustained increase in a specific subset of proinflammatory monocytes, with high TNF-α expression and an M1-like phenotype (independent of viral titers), in these previously healthy patients with severe disease. The relationship between M1-like monocytes and immunopathology was strengthened using murine models of influenza, in which severe infection generated using different models (including the high-pathogenicity H5N1 strain) was also accompanied by high levels of circulating M1-like monocytes. Additionally, a raised M1/M2 macrophage ratio in the lungs was observed. These studies identify a specific subtype of monocytes as a modifiable immunological determinant of disease severity in this subgroup of severely ill, previously healthy patients, offering potential novel therapeutic avenues.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures


References
-
- Influenza (Seasonal) Fact Sheet. World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs211/en/ Updated November 2016. Accessed March 8, 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/R502121/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U117585868/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_G1001212/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600371/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_12010/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_U117512723/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1001046/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1000758/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_UU_00008/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L018942/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0600520/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

