Myocardial oxidative stress correlates with left ventricular dysfunction on strain echocardiography in a rodent model of sepsis
- PMID: 28405943
- PMCID: PMC5389950
- DOI: 10.1186/s40635-017-0134-5
Myocardial oxidative stress correlates with left ventricular dysfunction on strain echocardiography in a rodent model of sepsis
Abstract
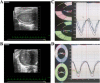
Background: Recognition of cardiomyopathy in sepsis can be challenging due to the limitations of conventional measures such as ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) in the context of variable preload and afterload conditions. This study correlates myocardial function using strain echocardiography (SE) with cardiomyocyte oxidative stress in a murine model of sepsis.
Methods: C57BL/6J mice were randomized into control (n = 10), sham (n = 25), and a cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) (n = 33) model of sepsis. Echocardiography was performed pre-, 12, 24, and 48 h post-injury. Cardiac pro-inflammatory cytokines and mitochondrial redox scavenger expression were evaluated in a subset of each arm. To evaluate the influence of redox scavenger upregulation on oxidative injury and cardiac function, CLP was performed on mitochondrial catalase-upregulated C57BL/6J MCAT+/+ mice (n = 12) and wild-type (WT) animals for comparison.
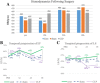
Results: Septic C57BL/6J mice exhibited depressed longitudinal strain (LS) when compared to sham and control at 24 h (p < 0.01) and 48 h (p = 0.04) post-CLP despite having a preserved EF. Furthermore, there was a significant association between increased odds of mortality and depressed LS (OR = 1.23, p = 0.04). Septic C57BL/6J mice concomitantly demonstrated increased expression of cardiomyocyte pro-inflammatory cytokines and decreased expression of redox scavengers at 24 and 48 h. When comparing C57Bl/6 MCAT +/+ mice and C57BL/6J WT mice, a significant decrease in LS was identified in the WT mice at 24 h (MCAT = -23 ± 5% vs. WT = -15 ± 4% p < 0.01) and 48 h (MCAT = -23 ± 7% vs. WT = -15 ± 4.3% p = 0.04) post-CLP which correlated with significant increase in the level of cardiac oxidative stress following CLP.
Conclusions: In this sepsis model, SE identified cardiomyopathy despite normal EF. SE depression temporally coincides with upregulation of inflammatory cytokines and decreases expression of key mitochondrial ROS scavengers. Upregulation of redox scavenger (CAT) abrogates oxidative stress and cardiac dysfunction in this sepsis model.
Keywords: Sepsis; Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction; Shock; Ultrasound.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Early markers of Sepsis Cardiomyopathy in Murine Models by Echocardiography.Curr Med Imaging. 2023 Apr 28. doi: 10.2174/1573405620666230428123541. Online ahead of print. Curr Med Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37132319
-
Myocardial Redox Hormesis Protects the Heart of Female Mice in Sepsis.Shock. 2019 Jul;52(1):52-60. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001245. Shock. 2019. PMID: 30102640
-
Myocardial Strain and Cardiac Output are Preferable Measurements for Cardiac Dysfunction and Can Predict Mortality in Septic Mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 May 21;8(10):e012260. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012260. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 31112430 Free PMC article.
-
Thioredoxin-1 attenuates sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy after cecal ligation and puncture in mice.J Surg Res. 2017 Dec;220:68-78. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2017.06.062. Epub 2017 Jul 25. J Surg Res. 2017. PMID: 29180214 Free PMC article.
-
A review of sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy.J Intensive Care. 2015 Nov 11;3:48. doi: 10.1186/s40560-015-0112-5. eCollection 2015. J Intensive Care. 2015. PMID: 26566443 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic Value of Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain in COVID-19.Am J Cardiol. 2020 Sep 15;131:134-136. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.06.053. Epub 2020 Jul 3. Am J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32732008 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Targeting cardiac resident CCR2+ macrophage-secreted MCP-1 to attenuate inflammation after myocardial infarction.Acta Biomater. 2024 Aug 23:S1742-7061(24)00469-0. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2024.08.025. Online ahead of print. Acta Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39182804
-
Recombinant human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 plays a protective role in mice with sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through multiple signaling pathways dependent on converting angiotensin II to angiotensin 1-7.Ann Transl Med. 2023 Jan 15;11(1):13. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-6016. Epub 2023 Jan 10. Ann Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36760245 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis-Induced Cardiomyopathy: Oxidative Implications in the Initiation and Resolution of the Damage.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:7393525. doi: 10.1155/2017/7393525. Epub 2017 Sep 19. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017. PMID: 29057035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GSDMD Mediates LPS-Induced Septic Myocardial Dysfunction by Regulating ROS-dependent NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 8;9:779432. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.779432. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34820388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M. The effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:15–21. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000194535.82812.BA. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

