Spatial relationship between Taenia solium tapeworm carriers and necropsy cyst burden in pigs
- PMID: 28406898
- PMCID: PMC5404875
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005536
Spatial relationship between Taenia solium tapeworm carriers and necropsy cyst burden in pigs
Abstract
Background: Taenia solium, a parasite that affects humans and pigs, is the leading cause of preventable epilepsy in the developing world. Geographic hotspots of pigs testing positive for serologic markers of T. solium exposure have been observed surrounding the locations of human tapeworm carriers. This clustered pattern of seropositivity in endemic areas formed the basis for geographically targeted control interventions, which have been effective at reducing transmission. In this study, we further explore the spatial relationship between human tapeworm carriers and infected pigs using necroscopic examination as a quantitative gold-standard diagnostic to detect viable T. solium cyst infection in pigs.
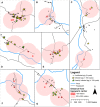
Methodology/principal findings: We performed necroscopic examinations on pigs from 7 villages in northern Peru to determine the number of viable T. solium cysts in each pig. Participating humans in the study villages were tested for T. solium tapeworm infection (i.e., taeniasis) with an ELISA coproantigen assay, and the distances from each pig to its nearest human tapeworm carrier were calculated. We assessed the relationship between proximity to a tapeworm carrier and the prevalence of light, moderate, and heavy cyst burden in pigs. The prevalence of pig infection was greatest within 50 meters of a tapeworm carrier and decreased monotonically as distance increased. Pigs living less than 50 meters from a human tapeworm carrier were 4.6 times more likely to be infected with at least one cyst than more distant pigs. Heavier cyst burdens, however, were not more strongly associated with proximity to tapeworm carriers than light cyst burdens.
Conclusion/significance: Our study shows that human tapeworm carriers and pigs with viable T. solium cyst infection are geographically correlated in endemic areas. This finding supports control strategies that treat humans and pigs based on their proximity to other infected individuals. We did not, however, find sufficient evidence that heavier cyst burdens in pigs would serve as improved targets for geographically focused control interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- International Task Force for Disease Eradication. Diseases considered as candidates for global eradication. 2008. Available from https://www.cartercenter.org/resources/pdfs/news/health_publications/itf...
-
- Coyle CM, Mahanty S, Zunt JR, Wallin MT, Cantey PT, White AC Jr. et al. Neurocysticercosis: neglected but not forgotten. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(5):e1500 doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001500 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bern C, Garcia HH, Evans C, Gonzalez AE, Verastegui M, Tsang VC et al. Magnitude of the disease burden from neurocysticercosis in a developing country. Clin Infect Dis 1999;29: 1203–1209. doi: 10.1086/313470 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- García HH, Gilman RH, Gonzalez AE, Verastegui M, Rodriguez S, Gavidia C, et al. Hyperendemic human and porcine Taenia solium infection in Perú. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003;68(3):268–75. - PubMed
-
- Komba EV, Kimbi EC, Ngowi HA, Kimera SI, Mlangwa JE, Lekule FP, et al. Prevalence of porcine cysticercosis and associated risk factors in smallholder pig production systems in Mbeya region, southern highlands of Tanzania. Vet Parasitol. 2013;198:284–291. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.09.020 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

