Dosimetric impacts of endorectal balloon in CyberKnife stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for early-stage prostate cancer
- PMID: 28407345
- PMCID: PMC5689864
- DOI: 10.1002/acm2.12063
Dosimetric impacts of endorectal balloon in CyberKnife stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for early-stage prostate cancer
Abstract
Purpose: In SBRT for prostate cancer, higher fractional dose to the rectum is a major toxicity concern due to using smaller PTV margin and hypofractionation. We investigate the dosimetric impact on rectum using endorectal balloon (ERB) in prostate SBRT.
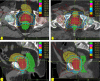
Materials and methods: Twenty prostate cancer patients were included in a retrospective study, ten with ERB and 10 without ERB. Optimized SBRT plans were generated on CyberKnife MultiPlan for 5 × 7.25 Gy to PTV under RTOG-0938 protocol for early-stage prostate cancer. For the rectum and the anterior half rectum, mean dose and percentage of volumes receiving 50%, 80%, 90%, and 100% prescription dose were compared.
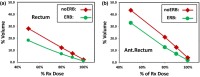
Results: Using ERB, mean dose to the rectum was 62 cGy (P = 0.001) lower per fraction, and 50 cGy (P = 0.024) lower per fraction for the anterior half rectum. The average V50% , V80% , V90% , and V100% were lower by 9.9% (P = 0.001), 5.3% (P = 0.0002), 3.4% (P = 0.0002), and 1.2% (P = 0.005) for the rectum, and lower by 10.4% (P = 0.009), 8.3% (P = 0.0004), 5.4% (P = 0.0003), and 2.1% (P = 0.003) for the anterior half rectum.
Conclusions: Significant reductions of dose to the rectum using ERB were observed. This may lead to improvement of the rectal toxicity profiles in prostate SBRT.
Keywords: SBRT; CyberKnife; endorectal balloon; prostate cancer; rectum toxicity.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Association of Physicists in Medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Brenner DJ, Hall EJ. Fractionation and protraction for radiotherapy of prostate carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1999;43:1095–1101. - PubMed
-
- Fowler JF. The radiobiology of prostate cancer including new aspects of fractionated radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2005;44:265–276. - PubMed
-
- Miralbell R, Roberts SA, Zubizarreta E, Hendry JH. Dose‐fractionation sensitivity of prostate cancer deduced from radiotherapy outcomes of 5,969 patients in seven international institutional datasets: Alpha/beta = 1.4 (0.9–2.2) Gy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82:e17–e24. - PubMed
-
- Langen KM, Willoughby TR, Meeks SL, et al. Observations on real‐time prostate gland motion using electromagnetic tracking. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;71:1084–1090. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

