KRAS G12C mutation as a poor prognostic marker of pemetrexed treatment in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 28407465
- PMCID: PMC5432792
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2015.299
KRAS G12C mutation as a poor prognostic marker of pemetrexed treatment in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background/aims: The predictive and prognostic value of KRAS mutation and its type of mutations in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are controversial. This clinical study was designed to investigate the predictive value of KRAS mutations and its mutation types to pemetrexed and gemcitabine based treatment.
Methods: Advanced NSCLC patients tested for KRAS mutation (n = 334) were retrospectively reviewed and 252 patients with wild type epidermal growth factor receptor and no anaplastic lymphoma kinase fusion were enrolled for the analysis. KRAS mutations were observed in 45 subjects with mutation type as followed: G12C (n = 13), G12D (n = 12), G12V (n = 12), other (n = 8). Response rate (RR), progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) of pemetrexed singlet and gemcitabine based chemotherapy were analysis.
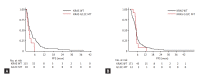
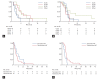
Results: Age, sex, performance status were well balanced between subjects with or without KRAS mutations. No difference was observed in RR. Hazard ratio (HR) of PFS for pemetrexed treated subjects with G12C mutation compared to subjects with KRAS wild type was 1.96 (95% confidential interval [CI], 1.01 to 3.79; p = 0.045), but other mutations failed to show clinical significance. By analysis done by PFS, compared to the subjects with transition mutation, HR was 1.48 (95% CI, 0.64 to 3.40; p = 0.360) for subjects with transversion mutation on pemetrexed treatment and 0.41 (95% CI, 0.19 to 0.87; p = 0.020) for subjects treated with gemcitabine based chemotherapy. No difference was observed in OS.
Conclusions: In this study, different drug sensitivity was observed according to the type of KRAS mutation. NSCLC subpopulations with different KRAS mutation type should be considered as different subgroups and optimal chemotherapy regimens should be searched in further confirmative studies.
Keywords: Carcinoma, non-small-cell lung; Gemcitabine; KRAS; Pemetrexed.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
Comment in
-
Realities of KRAS-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Korean J Intern Med. 2017 May;32(3):442. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2017.148. Epub 2017 Apr 28. Korean J Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28490719 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Rosell R, Carcereny E, Gervais R, et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): a multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13:239–246. - PubMed
-
- Solomon BJ, Mok T, Kim DW, et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2167–2177. - PubMed
-
- Suda K, Tomizawa K, Mitsudomi T. Biological and clinical significance of KRAS mutations in lung cancer: an oncogenic driver that contrasts with EGFR mutation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010;29:49–60. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
