Poly-GP in cerebrospinal fluid links C9orf72-associated dipeptide repeat expression to the asymptomatic phase of ALS/FTD
- PMID: 28408402
- PMCID: PMC5494528
- DOI: 10.15252/emmm.201607486
Poly-GP in cerebrospinal fluid links C9orf72-associated dipeptide repeat expression to the asymptomatic phase of ALS/FTD
Abstract
The C9orf72 GGGGCC repeat expansion is a major cause of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia (c9ALS/FTD). Non-conventional repeat translation results in five dipeptide repeat proteins (DPRs), but their clinical utility, overall significance, and temporal course in the pathogenesis of c9ALS/FTD are unclear, although animal models support a gain-of-function mechanism. Here, we established a poly-GP immunoassay from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to identify and characterize C9orf72 patients. Significant poly-GP levels were already detectable in asymptomatic C9orf72 mutation carriers compared to healthy controls and patients with other neurodegenerative diseases. The poly-GP levels in asymptomatic carriers were similar to symptomatic c9ALS/FTD cases. Poly-GP levels were not correlated with disease onset, clinical scores, and CSF levels of neurofilaments as a marker for axonal damage. Poly-GP determination in CSF revealed a C9orf72 mutation carrier in our cohort and may thus be used as a diagnostic marker in addition to genetic testing to screen patients. Presymptomatic expression of poly-GP and likely other DPR species may contribute to disease onset and thus represents an alluring therapeutic target.
Keywords: C9orf72; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; biomarker; cerebrospinal fluid; frontotemporal dementia.
© 2017 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Figures
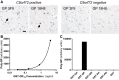
- A
Immunohistochemistry of frontal cortex from ALS/FTD cases with or without C9orf72 repeat expansion using poly‐GP antibodies 18H8 and 3F9. Both antibodies detect neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions specifically in the C9orf72 case (arrows). Hybridoma supernatants were used at 1:250 dilution as described previously (Schludi et al, 2015). Scale bar 20 μm.
- B, C
Poly‐GP sandwich immunoassay with anti‐GP antibodies 18H8 and 3F9 detects purified GST‐GP15 below 0.03 ng/ml (B), but no other 15‐mer DPRs fused to GST at 1 μg/ml. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 2) (C). A four‐parameter logistic curve was used to fit the dose–response using Prism 7.01 software.

- A–D
Poly‐GP sandwich immunoassay with anti‐GP antibodies 18H8 and 3F9 was used to analyze the GST‐GP15 standard at four concentrations. Background‐corrected absolute values, mean, and standard deviation (SD) for n = 4 GST‐GP15 intra‐plate replicates (A), n = 3 inter‐plate replicates (B), and n = 3 day‐to‐day replicates (C). Mean, SD, and the coefficient of variance (CV) for all conditions are listed in (D).
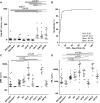
- A
Poly‐GP was measured using immunoassay in an age‐matched control population without signs of a neurodegenerative disease (ND‐CON, n = 18–20), C9orf72‐negative offspring of C9orf72 mutation carriers (NonC9‐F1, n = 8) in patients with other neurodegenerative diseases, that is, Alzheimer's (AD, n = 24) and Parkinson's disease (PD, n = 14), sporadic ALS (sALS, n = 18) and FTD (sFTD, n = 11) patients, and asymptomatic (C9‐F1, n = 10) and symptomatic C9orf72 mutation carriers with ALS (c9ALS, n = 9) and FTD (c9FTD, n = 11). The c9FTD patient indicated by the filled, red circle was initially seen under the differential diagnosis of AD, but after poly‐GP measurement followed by C9orf72 genotyping reclassified as c9FTD.
- B
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis of poly‐GP levels for the discrimination of C9orf72 mutation carriers vs. non‐carriers. The cutoff (43.5) was calculated using the Youden index and is shown as a dotted line in (A). AUC, area under the curve; Sens, sensitivity; Spec, specificity.
- C, D
(C) Phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain (pNfH) and (D) neurofilament light chain (NfL) were measured using an established ELISA.
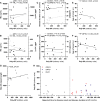
- A–F
Correlation analysis of poly‐GP levels in CSF of c9ALS (A, C, E) and c9FTD cases (B, D, F). Correlation with phosphorylated neurofilament heavy chain (pNfH) and neurofilament light chain (NfL) (A, B), with disease duration at lumbar puncture (LP) and the ALSFRS‐R or FTLD‐CDR score (C, D) and with age at disease onset (E, F).
- G
Correlation of poly‐GP levels in CSF with the largest repeat length estimated by Southern blotting.
- H
Association of poly‐GP levels in CSF with disease duration at LP in c9ALS/FTD patients and with time to expected disease onset in C9‐F1 cases. Time to expected disease onset was calculated using parental age at disease onset.
Comment in
-
Specific biomarkers for C9orf72 FTD/ALS could expedite the journey towards effective therapies.EMBO Mol Med. 2017 Jul;9(7):853-855. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201707848. EMBO Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28533210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akimoto C, Volk AE, van Blitterswijk M, Van den Broeck M, Leblond CS, Lumbroso S, Camu W, Neitzel B, Onodera O, van Rheenen W et al (2014) A blinded international study on the reliability of genetic testing for GGGGCC‐repeat expansions in C9orf72 reveals marked differences in results among 14 laboratories. J Med Genet 51: 419–424 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al‐Sarraj S, King A, Troakes C, Smith B, Maekawa S, Bodi I, Rogelj B, Al‐Chalabi A, Hortobagyi T, Shaw CE (2011) p62 positive, TDP‐43 negative, neuronal cytoplasmic and intranuclear inclusions in the cerebellum and hippocampus define the pathology of C9orf72‐linked FTLD and MND/ALS. Acta Neuropathol 122: 691–702 - PubMed
-
- Baborie A, Griffiths TD, Jaros E, Perry R, McKeith IG, Burn DJ, Masuda‐Suzukake M, Hasegawa M, Rollinson S, Pickering‐Brown S et al (2014) Accumulation of dipeptide repeat proteins predates that of TDP‐43 in Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration associated with hexanucleotide repeat expansions in C9ORF72 gene. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 41: 601–612 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Beck J, Poulter M, Hensman D, Rohrer JD, Mahoney CJ, Adamson G, Campbell T, Uphill J, Borg A, Fratta P et al (2013) Large C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansions are seen in multiple neurodegenerative syndromes and are more frequent than expected in the UK population. Am J Hum Genet 92: 345–353 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

