Multidirectional Shoulder Instability: Arthroscopic Labral Augmentation
- PMID: 28409104
- PMCID: PMC5382315
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2016.09.025
Multidirectional Shoulder Instability: Arthroscopic Labral Augmentation
Abstract
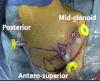
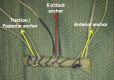
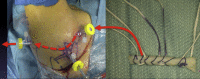
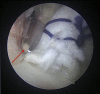
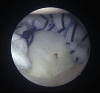
Capsulolabral augmentation is one of the most used arthroscopic techniques to address multidirectional instability of the shoulder. Given the thin and weak capsule seen in the affected patients, reconstruction in this subset of patients can be particularly challenging. This arthroscopic technique aims to reduce the capsular volume and deepen the glenoid socket through the creation of a particularly voluminous "bumper" along the glenoid bone. Increasing the depth of the glenoid facilitates a concavity-compression stabilizing effect and, therefore, shoulder stability, especially midrange stability. This technique aims to augment the bump of the standard capsulolabral reconstruction by using a resorbable surgical mesh derived from porcine skin.
Figures





References
-
- Gaskill T.R., Taylor D.C., Millet P.J. Management of multidirectional instability of the shoulder. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2011;19:758–767. - PubMed
-
- Metcalf M.H., Pon D.J., Harryman D.T., II Capsulolabral augmentation increase glenohumeral stability in the cadaver shoulder. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2001;10:532–538. - PubMed
-
- Apostolakos J., Yang J.S., Hoberman A.R. Glenoid labrum. In: Bain G.I., Itoi E., Di Giacomo G., Sugaya H., editors. Normal and pathological anatomy of the shoulder. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 2015. pp. 83–91.
-
- Warner J.J., Bowen M.K., Deng X., Torzilli P.A., Warren R.F. Effect of joint compression on inferior stability of the glenohumeral joint. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1999;11:141–149. - PubMed
-
- Lippitt S.B., Vanderhooft J.E., Harris S.L., Sidles J.A., Harryman D.T., Matsen F.A. Glenohumeral stability from concavity-compression: A quantitative analysis. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 1993;2:27–35. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

