Antiplatelet and anti-proliferative action of disintegrin from Echis multisquamatis snake venom
- PMID: 28409495
- PMCID: PMC5410738
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2017.58.118
Antiplatelet and anti-proliferative action of disintegrin from Echis multisquamatis snake venom
Abstract
Aim: To purify the platelet aggregation inhibitor from Echis multisquamatis snake venom (PAIEM) and characterize its effect on platelet aggregation and HeLa cell proliferation.
Methods: Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) were used for PAIEM identification. Platelet aggregation in the presence of PAIEM was studied on aggregometer Solar-AP2110. The changes of shape and granularity of platelets in the presence of PAIEM were studied on flow cytometer COULTER EPICS XL, and degranulation of platelets was estimated using spectrofluorimetry. Indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used for the determination of target of PAIEM on platelet surface. An assay based on 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide was used to evaluate the effect of PAIEM on the proliferation of HeLa cells in cell culture.
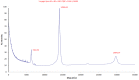
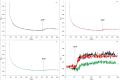
Results: The molecular weight of the protein purified from Echis multisquamatis venom was 14.9 kDa. Half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of PAIEM needed to inhibit adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-induced platelet aggregation was 7 μM. PAIEM did not affect thrombin- or ADP-induced platelet activation, but it did prevent binding of the anti-IIb antibody to glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GPIIbIIIa)-receptor of adhered platelets and inhibited the viability of HeLa cells by 54%.
Conclusion: As a member of the disintegrin family, PAIEM inhibited platelet aggregation and cell proliferation possibly by blocking integrin-mediated interactions. However, it did not impair cellular signaling causing any changes in platelet shape and granularity and did not affect ADP-induced platelet degranulation. This disintegrin was shown to be a potent inhibitor of integrin-mediated cellular interactions including platelet aggregation or cancer cell proliferation.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

