Identification of myoelectric signals of pregnant rat uterus: new method to detect myometrial contraction
- PMID: 28409497
- PMCID: PMC5410739
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2017.58.141
Identification of myoelectric signals of pregnant rat uterus: new method to detect myometrial contraction
Abstract
Aim: To develop an electromyography method for pregnant rat uterus in vivo and to separate myometrial signals from the gastrointestinal tract signals.
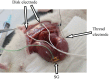
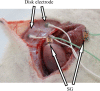
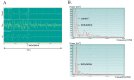
Methods: Pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats (n=8) were anaesthetized and their stomach, small intestine, and large intestine were removed from the abdomen. A pair of thread electrodes was inserted into the uterus, while a pair of disk electrodes was placed subcutaneously above the myometrium. Additionally, a strain gauge sensor was fixed on the surface of the myometrium and cecum for the parallel detection of mechanical contractions in rats (n=18) with intact gastrointestinal tract. The filtered electric signals were amplified and recorded by an online computer system and analyzed by fast Fourier transformation. The frequency of the electric activity was characterized by cycle per minute (cpm), the magnitude of the activity was described as power spectrum density maximum (PsDmax).
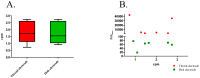
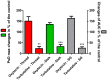
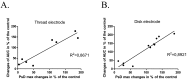
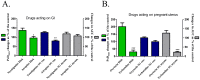
Results: The frequency of the pregnant uterine activity was 1-3 cpm, which falls within the same range as that of cecum. Measuring by both electrodes, oxytocin (1 µg/kg) increased and terbutaline (50 µg/kg) decreased the PsDmax by 25%-50% (P<0.001) and 25%-40% (P<0.01), respectively. We found a strong positive correlation between the alterations of PsDmax values and the strain gauge sensor-detected mechanical contractions (area under curve). The GI specific compounds (neostigmine, atropine) mainly affected the cecal activity, while myometrium specific drugs (oxytocin, terbutaline) influenced the myometrial signals only. Conclusion Our method proved to be able to detect the myoelectric activity that reflects the mechanical contraction. The overlapping myometrial and cecal signals are not separable, but they can be distinguished based on the much higher activity and different pharmacological reactivity of the pregnant uterus. Thus, the early signs of contractions can be detected and labor may be predicted in a fast and sensitive way.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between slow-wave myoelectric signals and mechanical contractions in the gastrointestinal tract: Advanced electromyographic method in rats.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2016 Nov-Dec;82:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2016.07.005. Epub 2016 Jul 27. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27475721
-
Effect of stimulatory and inhibitory drugs on uterine electrical activity measured noninvasively from the abdominal surface of pregnant rats.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Jul;183(1):68-75. doi: 10.1067/mob.2000.105348. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000. PMID: 10920311
-
The role of diacylglycerol as a modulator of oxytocin-stimulated phasic contractions in myometrium from pregnant and nonpregnant rats.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000 Apr;182(4):943-9. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(00)70351-6. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000. PMID: 10764478
-
Integration of endocrine and mechanical signals in the regulation of myometrial functions during pregnancy and labour.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009 May;144 Suppl 1:S2-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2009.02.044. Epub 2009 Mar 18. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2009. PMID: 19299064 Review.
-
Review and Study of Uterine Bioelectrical Waveforms and Vector Analysis to Identify Electrical and Mechanosensitive Transduction Control Mechanisms During Labor in Pregnant Patients.Reprod Sci. 2021 Mar;28(3):838-856. doi: 10.1007/s43032-020-00358-5. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Reprod Sci. 2021. PMID: 33090378 Review.
Cited by
-
Prediction of gastroesophageal reflux episodes by smooth muscle electromyography: A translational study in rats and adolescents.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 9;9(8):e18859. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e18859. eCollection 2023 Aug. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37609397 Free PMC article.
-
Smooth muscle electromyography for detecting major alterations in the estrus cycle in rats.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 8;19(8):e0307932. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307932. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39116057 Free PMC article.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acid Consumption Alters Uterine Contraction: A Comparative Study on Different Breeds of Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 29;26(11):5221. doi: 10.3390/ijms26115221. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40508030 Free PMC article.
-
The combined uterorelaxant effect of sildenafil and terbutalin in the rat: The potential benefit of co-administration of low doses.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 17;9(12):e22488. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22488. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38046168 Free PMC article.
-
Combined uterorelaxant effect of magnesium sulfate and terbutaline: Studies on late pregnant rat uteri in vitro and in vivo.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2023 Apr;102(4):457-464. doi: 10.1111/aogs.14532. Epub 2023 Feb 19. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2023. PMID: 36808376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fernández-Martinez E, Ponce-Monter H, Soria-Jasso LE, Ortiz MI, Arias-Montano JA, Barragan-Ramirez G, et al. Inhibition of uterine contractility by thalidomide analogs via phosphodiesterase-4 inhibition and calcium entry blockade. Molecules. 2016;21:1332. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101332. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

