The "Iron"-y of Iron Overload and Iron Deficiency in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
- PMID: 28410559
- PMCID: PMC5694836
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201702-0311PP
The "Iron"-y of Iron Overload and Iron Deficiency in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
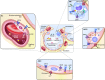
Figures

References
-
- Mannino DM, Buist AS. Global burden of COPD: risk factors, prevalence, and future trends. Lancet. 2007;370:765–773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PG/15/56/31573 /BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- 093080/Z/10/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R00 HL125899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/14/27/30679 /BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- R368/0714/DMT_/The Dunhill Medical Trust/United Kingdom
- P01 HL105339/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL125899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G1001367/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL055330/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/14/27/30679/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- P01 HL114501/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- PG/15/56/31573/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- G1000758/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HL079904/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

