Liquid biopsy: a step forward towards precision medicine in urologic malignancies
- PMID: 28410618
- PMCID: PMC5391592
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0644-5
Liquid biopsy: a step forward towards precision medicine in urologic malignancies
Abstract
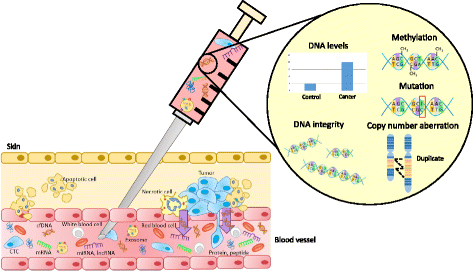
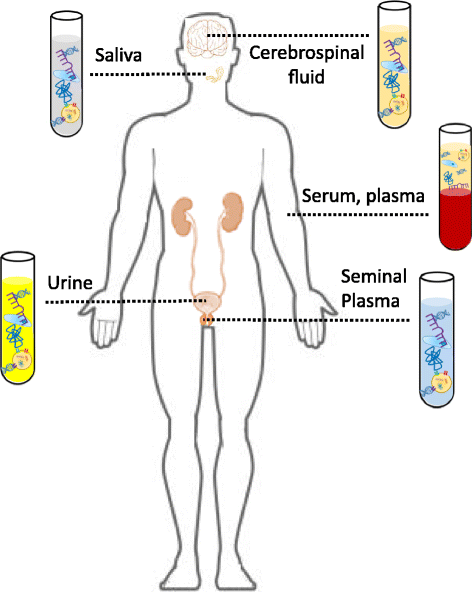
There is a growing trend towards exploring the use of a minimally invasive "liquid biopsy" to identify biomarkers in a number of cancers, including urologic malignancies. Multiple aspects can be assessed in circulating cell-free DNA, including cell-free DNA levels, integrity, methylation and mutations. Other prospective liquid biopsy markers include circulating tumor cells, circulating RNAs (miRNA, lncRNAs and mRNAs), cell-free proteins, peptides and exosomes have also emerged as non-invasive cancer biomarkers. These circulating molecules can be detected in various biological fluids, including blood, urine, saliva and seminal plasma. Liquid biopsies hold great promise for personalized medicine due to their ability to provide multiple non-invasive global snapshots of the primary and metastatic tumors. Molecular profiling of circulating molecules has been a stepping-stone to the successful introduction of several non-invasive multi-marker tests into the clinic. In this review, we provide an overview of the current state of cell-free DNA-based kidney, prostate and bladder cancer biomarker research and discuss the potential utility other circulating molecules. We will also discuss the challenges and limitations facing non-invasive cancer biomarker discovery and the benefits of this growing area of translational research.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Bladder cancer; Cancer treatment; Cell-free DNA; Circulating tumor DNA; Circulating tumor cells; Exosomse; Kidney cancer; Liquid biopsy; Long non-coding RNA; Personalized medicine; Precision medicine; Predictive markers; Prostate cancer; Tumor markers; miRNAs.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

