Frontotemporal Dementia
- PMID: 28410663
- PMCID: PMC5472209
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncl.2017.01.008
Frontotemporal Dementia
Abstract
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a heterogeneous disorder with distinct clinical phenotypes associated with multiple neuropathologic entities. Presently, the term FTD encompasses clinical disorders that include changes in behavior, language, executive control, and often motor symptoms. The core FTD spectrum disorders include behavioral variant FTD, nonfluent/agrammatic variant primary progressive aphasia, and semantic variant PPA. Related FTD disorders include frontotemporal dementia with motor neuron disease, progressive supranuclear palsy syndrome, and corticobasal syndrome. In this article, the authors discuss the clinical presentation, diagnostic criteria, neuropathology, genetics, and treatments of these disorders.
Keywords: Corticobasal syndrome (CBS); Frontotemporal dementia (FTD); Motor neuron disease; Nonfluent PPA; Primary progressive aphasia; Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP); Semantic PPA.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
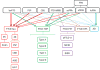
Figures
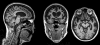

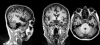
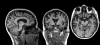







References
-
- Alzheimer A. Uber eigenartige Krankheitsfalle des spateren Alters. Z Gesamte Neruol Psychiatr. 1911;4:356–385.
-
- Ames D, Cummings JL, Wirshing WC, Quinn B, Mahler M. Repetitive and compulsive behavior in frontal lobe degenerations. Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 1994;6(2):100–113. - PubMed
-
- Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Oda T. TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;351(3):602–611. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

