Antagonism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in medial prefrontal cortex disrupts the context preexposure facilitation effect
- PMID: 28411153
- PMCID: PMC5540765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.04.003
Antagonism of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in medial prefrontal cortex disrupts the context preexposure facilitation effect
Abstract
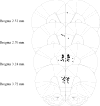
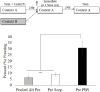
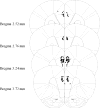
Cholinergic function plays a role in a variant of context fear conditioning known as the context preexposure facilitation effect (CPFE; Robinson-Drummer, Dokovna, Heroux, & Stanton, 2016). In the CPFE, acquisition of a context representation, the context-shock association, and expression of context fear occur across successive phases, usually 24h apart. Systemic administration of scopolamine, a muscarinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist, prior to each phase (context preexposure, immediate-shock training, and testing) disrupts the CPFE in juvenile rats (Robinson-Drummer et al., 2016). Dorsal hippocampal (dHPC) cholinergic function contributes significantly to this effect, as local infusion of scopolamine into the dHPC prior to any individual phase of the CPFE produces a disruption identical to systemic administration (Robinson-Drummer et al., 2016). The current experiment extended these findings to another forebrain region implicated in the CPFE, the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC). Adolescent rats received bilateral infusions of scopolamine (35μg/side) or PBS 10min before all three phases of the CPFE or only prior to a single phase. Intra-mPFC administration of scopolamine prior to all three phases significantly impaired fear conditioning suggesting that mPFC cholinergic function is necessary for successful CPFE performance. Analyses of the individual infusion days revealed a significant impairment of the CPFE when infusions occurred prior to preexposure or training (i.e. immediate footshock) but not prior to testing. In total, these findings suggests a role of mPFC cholinergic function in the acquisition and/or consolidation of a contextual representation and the context-shock association but not in retrieval or expression of fear memory. Implications for mPFC involvement in contextual fear conditioning and neurological dysfunction following neonatal alcohol exposure are discussed.
Keywords: CPFE; Fear; Muscarinic; Prefrontal; Spatial learning.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Prefrontal NMDA-receptor antagonism disrupts encoding or consolidation but not retrieval of incidental context learning.Behav Brain Res. 2021 May 7;405:113175. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113175. Epub 2021 Feb 14. Behav Brain Res. 2021. PMID: 33596432
-
Medial prefrontal and ventral hippocampal contributions to incidental context learning and memory in adolescent rats.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019 Dec;166:107091. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2019.107091. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2019. PMID: 31542328
-
Role of dorsal and ventral hippocampal muscarinic receptor activity in acquisition and retention of contextual fear conditioning.Behav Neurosci. 2020 Oct;134(5):460-470. doi: 10.1037/bne0000411. Behav Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33001682
-
The role of the medial prefrontal cortex in the generalization of conditioned fear.Neuropsychology. 2018 Jan;32(1):1-17. doi: 10.1037/neu0000384. Epub 2017 Aug 31. Neuropsychology. 2018. PMID: 28857602 Review.
-
Antidepressant effects of the muscarinic cholinergic receptor antagonist scopolamine: a review.Biol Psychiatry. 2013 Jun 15;73(12):1156-63. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.09.031. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Biol Psychiatry. 2013. PMID: 23200525 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distinct patterns of brain Fos expression in Carioca High- and Low-conditioned Freezing Rats.PLoS One. 2020 Jul 23;15(7):e0236039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0236039. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32702030 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal ethanol exposure impairs long-term context memory formation and prefrontal immediate early gene expression in adolescent rats.Behav Brain Res. 2019 Feb 1;359:386-395. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2018.11.018. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Behav Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30447241 Free PMC article.
-
Examination of cortically projecting cholinergic neurons following exercise and environmental intervention in a rodent model of fetal alcohol spectrum disorders.Birth Defects Res. 2021 Feb 1;113(3):299-313. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.1839. Epub 2020 Nov 10. Birth Defects Res. 2021. PMID: 33174398 Free PMC article.
-
Ventral Hippocampal Input to the Prelimbic Cortex Dissociates the Context from the Cue Association in Trace Fear Memory.J Neurosci. 2020 Apr 15;40(16):3217-3230. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1453-19.2020. Epub 2020 Mar 18. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32188770 Free PMC article.
-
Augmentation of Exposure Therapy With Cholinergic Blockade: Promising Novel Approach or Too Early to Tell?Biol Psychiatry. 2019 Nov 1;86(9):654-656. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.08.008. Biol Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31601363 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brito GN, Davis BJ, Stopp LC, Stanton ME. Memory and the septo-hippocampal cholinergic system in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1983;81(4):315–320. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

