Liver Metastasis and Treatment Outcome with Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibody in Patients with Melanoma and NSCLC
- PMID: 28411193
- PMCID: PMC5749922
- DOI: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-16-0325
Liver Metastasis and Treatment Outcome with Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibody in Patients with Melanoma and NSCLC
Abstract
We explored the association between liver metastases, tumor CD8+ T-cell count, and response in patients with melanoma or lung cancer treated with the anti-PD-1 antibody, pembrolizumab. The melanoma discovery cohort was drawn from the phase I Keynote 001 trial, whereas the melanoma validation cohort was drawn from Keynote 002, 006, and EAP trials and the non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cohort from Keynote 001. Liver metastasis was associated with reduced response and shortened progression-free survival [PFS; objective response rate (ORR), 30.6%; median PFS, 5.1 months] compared with patients without liver metastasis (ORR, 56.3%; median PFS, 20.1 months) P ≤ 0.0001, and confirmed in the validation cohort (P = 0.0006). The presence of liver metastasis significantly increased the likelihood of progression (OR, 1.852; P < 0.0001). In a subset of biopsied patients (n = 62), liver metastasis was associated with reduced CD8+ T-cell density at the invasive tumor margin (liver metastasis+ group, n = 547 ± 164.8; liver metastasis- group, n = 1,441 ± 250.7; P < 0.016). A reduced response rate and shortened PFS was also observed in NSCLC patients with liver metastasis [median PFS, 1.8 months; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.4-2.0], compared with those without liver metastasis (n = 119, median PFS, 4.0 months; 95% CI, 2.1-5.1), P = 0.0094. Thus, liver metastatic patients with melanoma or NSCLC that had been treated with pembrolizumab were associated with reduced responses and PFS, and liver metastases were associated with reduced marginal CD8+ T-cell infiltration, providing a potential mechanism for this outcome. Cancer Immunol Res; 5(5); 417-24. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
M.D. Hellmann reports receiving other commercial research support from BMS and Genentech and is a consultant/advisory board member for AstraZeneca, BMS, Genentech, Janssen, Merck, and Novartis. O. Hamid has received speakers bureau honoraria from Amgen, BMS, Genentech, and Novartis, is a consultant/advisory board member for Amgen, BMS, Merck, Novartis, and Roche. M.A. Gubens is a consultant/advisory board member for BMS. J.M. Taube reports receiving a commercial research grant from Bristol-Myers Squibb and is a consultant/advisory board member for Astra Zeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Merck. E.J. Taylor is the chief executive officer at Naked Biome. B. Chmielowski has received speakers bureau honoraria from Genentech and Janssen, is a consultant/advisory board member for Amgen, Astellas, BMS, Eisai, Genentech, Immunocore, Lilly, andMerck. R. Dummer is a consultant/advisory board member for BMS and MSD. S.M. Goldinger is a consultant/advisory board member for BMS, MSD, Novaertis, and Roche. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures




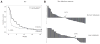
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

