Systematic characterization of A-to-I RNA editing hotspots in microRNAs across human cancers
- PMID: 28411194
- PMCID: PMC5495064
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.219741.116
Systematic characterization of A-to-I RNA editing hotspots in microRNAs across human cancers
Abstract
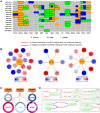
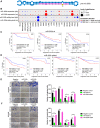
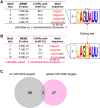
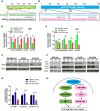
RNA editing, a widespread post-transcriptional mechanism, has emerged as a new player in cancer biology. Recent studies have reported key roles for individual miRNA editing events, but a comprehensive picture of miRNA editing in human cancers remains largely unexplored. Here, we systematically characterized the miRNA editing profiles of 8595 samples across 20 cancer types from miRNA sequencing data of The Cancer Genome Atlas and identified 19 adenosine-to-inosine (A-to-I) RNA editing hotspots. We independently validated 15 of them by perturbation experiments in several cancer cell lines. These miRNA editing events show extensive correlations with key clinical variables (e.g., tumor subtype, disease stage, and patient survival time) and other molecular drivers. Focusing on the RNA editing hotspot in miR-200b, a key tumor metastasis suppressor, we found that the miR-200b editing level correlates with patient prognosis opposite to the pattern observed for the wild-type miR-200b expression. We further experimentally showed that, in contrast to wild-type miRNA, the edited miR-200b can promote cell invasion and migration through its impaired ability to inhibit ZEB1/ZEB2 and acquired concomitant ability to repress new targets, including LIFR, a well-characterized metastasis suppressor. Our study highlights the importance of miRNA editing in gene regulation and suggests its potential as a biomarker for cancer prognosis and therapy.
© 2017 Wang et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Attenuated adenosine-to-inosine editing of microRNA-376a* promotes invasiveness of glioblastoma cells.J Clin Invest. 2012 Nov;122(11):4059-76. doi: 10.1172/JCI62925. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Clin Invest. 2012. PMID: 23093778 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR1-mediated RNA editing is a novel oncogenic process in thyroid cancer and regulates miR-200 activity.Oncogene. 2020 Apr;39(18):3738-3753. doi: 10.1038/s41388-020-1248-x. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Oncogene. 2020. PMID: 32157211 Free PMC article.
-
ADAR2/miR-589-3p axis controls glioblastoma cell migration/invasion.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Feb 28;46(4):2045-2059. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1257. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29267965 Free PMC article.
-
The adaptive potential of RNA editing-mediated miRNA-retargeting in cancer.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019 Mar;1862(3):291-300. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2018.12.007. Epub 2018 Dec 31. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2019. PMID: 30605729 Review.
-
When MicroRNAs Meet RNA Editing in Cancer: A Nucleotide Change Can Make a Difference.Bioessays. 2018 Feb;40(2):10.1002/bies.201700188. doi: 10.1002/bies.201700188. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Bioessays. 2018. PMID: 29280160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pan-Cancer Analysis of Canonical and Modified miRNAs Enhances the Resolution of the Functional miRNAome in Cancer.Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 17;82(20):3687-3700. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0240. Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36040379 Free PMC article.
-
The microRNA Lifecycle in Health and Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;14(23):5748. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235748. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics of Adenosine-to-Inosine RNA editing-based subtypes and novel risk score for the prognosis and drug sensitivity in stomach adenocarcinoma.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 1;10:1073688. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1073688. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36531956 Free PMC article.
-
The Butterfly Effect of RNA Alterations on Transcriptomic Equilibrium.Cells. 2019 Dec 13;8(12):1634. doi: 10.3390/cells8121634. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31847302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unifying Different Cancer Theories in a Unique Tumour Model: Chronic Inflammation and Deaminases as Meeting Points.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 5;23(15):8720. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158720. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955853 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alon S, Erew M, Eisenberg E. 2015. DREAM: a webserver for the identification of editing sites in mature miRNAs using deep sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31: 2568–2570. - PubMed
-
- Bailey TL, Elkan C. 1994. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc Int Conf Intellt Syst Mol Biol 2: 28–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
