mTORC1 signaling and the metabolic control of cell growth
- PMID: 28411448
- PMCID: PMC5545101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceb.2017.02.012
mTORC1 signaling and the metabolic control of cell growth
Abstract
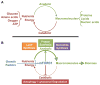
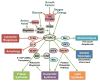
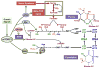
mTOR [mechanistic target of rapamycin] is a serine/threonine protein kinase that, as part of mTORC1 (mTOR complex 1), acts as an important molecular connection between nutrient signals and the metabolic processes indispensable for cell growth. While there has been pronounced interest in the upstream mechanisms regulating mTORC1, the full range of downstream molecular targets through which mTORC1 signaling stimulates cell growth is only recently emerging. It is now evident that mTORC1 promotes cell growth primarily through the activation of key anabolic processes. Through a diverse set of downstream targets, mTORC1 promotes the biosynthesis of macromolecules, including proteins, lipids, and nucleotides to build the biomass underlying cell, tissue, and organismal growth. Here, we focus on the metabolic functions of mTORC1 as they relate to the control of cell growth. As dysregulated mTORC1 underlies a variety of human diseases, including cancer, diabetes, autoimmune diseases, and neurological disorders, understanding the metabolic program downstream of mTORC1 provides insights into its role in these pathological states.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

