Engineered Exosomes as Vehicles for Biologically Active Proteins
- PMID: 28412169
- PMCID: PMC5474961
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.030
Engineered Exosomes as Vehicles for Biologically Active Proteins
Abstract
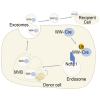
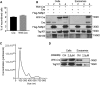
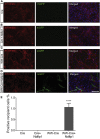
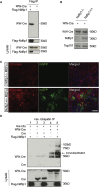
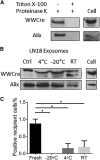
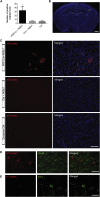
Exosomes represent an attractive vehicle for the delivery of biomolecules. However, mechanisms for loading functional molecules into exosomes are relatively unexplored. Here we report the use of the evolutionarily conserved late-domain (L-domain) pathway as a mechanism for loading exogenous proteins into exosomes. We demonstrate that labeling of a target protein, Cre recombinase, with a WW tag leads to recognition by the L-domain-containing protein Ndfip1, resulting in ubiquitination and loading into exosomes. Our results show that Ndfip1 expression acts as a molecular switch for exosomal packaging of WW-Cre that can be suppressed using the exosome inhibitor GW4869. When taken up by floxed reporter cells, exosomes containing WW-Cre were capable of inducing DNA recombination, indicating functional delivery of the protein to recipient cells. Engineered exosomes were administered to the brain of transgenic reporter mice using the nasal route to test for intracellular protein delivery in vivo. This resulted in the transport of engineered exosomes predominantly to recipient neurons in a number of brain regions, including the olfactory bulb, cortex, striatum, hippocampus, and cerebellum. The ability to engineer exosomes to deliver biologically active proteins across the blood-brain barrier represents an important step for the development of therapeutics to treat brain diseases.
Keywords: ESCRT; L-domain; blood-brain barrier; drug delivery; extracellular vesicles; intraluminal vesicles; nasal delivery; therapy; ubiquitin.
Copyright © 2017 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Ticket to Ride: Targeting Proteins to Exosomes for Brain Delivery.Mol Ther. 2017 Jun 7;25(6):1264-1266. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.05.001. Epub 2017 May 10. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28499750 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Exosome delivered anticancer drugs across the blood-brain barrier for brain cancer therapy in Danio rerio.Pharm Res. 2015 Jun;32(6):2003-14. doi: 10.1007/s11095-014-1593-y. Epub 2015 Jan 22. Pharm Res. 2015. PMID: 25609010 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudotyping exosomes for enhanced protein delivery in mammalian cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2017 Apr 18;12:3153-3170. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S133430. eCollection 2017. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28458537 Free PMC article.
-
Nedd4 family-interacting protein 1 (Ndfip1) is required for the exosomal secretion of Nedd4 family proteins.J Biol Chem. 2008 Nov 21;283(47):32621-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M804120200. Epub 2008 Sep 25. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18819914
-
Targeted therapeutic delivery using engineered exosomes and its applications in cardiovascular diseases.Gene. 2016 Jan 10;575(2 Pt 2):377-384. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2015.08.067. Epub 2015 Sep 2. Gene. 2016. PMID: 26341056 Review.
-
Exosomes as drug delivery vehicles and biomarkers for neurological and auditory systems.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Dec;236(12):8035-8049. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30484. Epub 2021 Jul 5. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34224589 Review.
Cited by
-
The Mystery of Red Blood Cells Extracellular Vesicles in Sleep Apnea with Metabolic Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4301. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094301. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919065 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting Manipulated Small Extracellular Vesicles to Subvert Immunosuppression at the Tumor Microenvironment through Mannose Receptor/CD206 Targeting.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 31;21(17):6318. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176318. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32878276 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review: Milk Small Extracellular Vesicles for Use in the Delivery of Therapeutics.Pharm Res. 2023 Apr;40(4):909-915. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03404-w. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 36198923 Review.
-
The potential therapeutic value and application prospect of engineered exosomes in human diseases.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 1;10:1051380. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1051380. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36531952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current and Emerging Strategies for Enhancing Antibody Delivery to the Brain.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Nov 26;13(12):2014. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13122014. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34959296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Simons M., Raposo G. Exosomes—vesicular carriers for intercellular communication. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009;21:575–581. - PubMed
-
- EL Andaloussi S., Mäger I., Breakefield X.O., Wood M.J. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013;12:347–357. - PubMed
-
- Vlassov A.V., Magdaleno S., Setterquist R., Conrad R. Exosomes: current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012;1820:940–948. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

