Lipid Nanoparticle Systems for Enabling Gene Therapies
- PMID: 28412170
- PMCID: PMC5498813
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.013
Lipid Nanoparticle Systems for Enabling Gene Therapies
Abstract
Genetic drugs such as small interfering RNA (siRNA), mRNA, or plasmid DNA provide potential gene therapies to treat most diseases by silencing pathological genes, expressing therapeutic proteins, or through gene-editing applications. In order for genetic drugs to be used clinically, however, sophisticated delivery systems are required. Lipid nanoparticle (LNP) systems are currently the lead non-viral delivery systems for enabling the clinical potential of genetic drugs. Application will be made to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2017 for approval of an LNP siRNA drug to treat transthyretin-induced amyloidosis, presently an untreatable disease. Here, we first review research leading to the development of LNP siRNA systems capable of silencing target genes in hepatocytes following systemic administration. Subsequently, progress made to extend LNP technology to mRNA and plasmids for protein replacement, vaccine, and gene-editing applications is summarized. Finally, we address current limitations of LNP technology as applied to genetic drugs and ways in which such limitations may be overcome. It is concluded that LNP technology, by virtue of robust and efficient formulation processes, as well as advantages in potency, payload, and design flexibility, will be a dominant non-viral technology to enable the enormous potential of gene therapy.
Keywords: gene editing; gene therapy; genetic drugs; lipid nanoparticles; mRNA; siRNA.
Copyright © 2017 The American Society of Gene and Cell Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
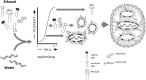
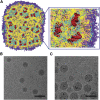

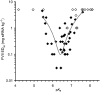
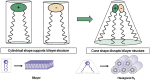
References
-
- Cullis P.R., Mayer L.D., Bally M.B., Madden T.D., Hope M.J. Generating and loading of liposomal systems for drug-delivery applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1989;3:267–282.
-
- Cullis P.R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1979;559:399–420. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

