Effects of Regulatory Support Services on Institutional Review Board Turnaround Times
- PMID: 28412874
- PMCID: PMC5546085
- DOI: 10.1177/1556264617704294
Effects of Regulatory Support Services on Institutional Review Board Turnaround Times
Abstract
We evaluated how regulatory support services provided by University of Illinois at Chicago's Center for Clinical and Translational Science may reduce Institutional Review Board (IRB) turnaround times. IRB applications were categorized by receipt of any regulatory support and amount of support received. Turnaround time included total turnaround time, time for IRB review, and time for investigators to modify protocols. There were no differences in any turnaround times for supported versus nonsupported applications. However, for supported applications, those receiving more intensive support had total turnaround times 16.0 days ( SE 7.62, p < .05) faster than those receiving less intensive support. Receiving higher regulatory support may be associated with faster approval of IRB submissions.
Keywords: CTSA evaluation; Institutional Review Boards; clinical research; evaluation research; translational research.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
Figures

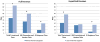
Similar articles
-
The Real-Time IRB: A Collaborative Innovation to Decrease IRB Review Time.J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018 Oct;13(4):432-437. doi: 10.1177/1556264618780803. Epub 2018 Jun 14. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018. PMID: 29902956 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Support Improves Subsequent IRB Approval Rates in Studies Initially Deemed Not Ready for Review: A CTSA Institution's Experience.J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018 Apr;13(2):139-144. doi: 10.1177/1556264617752725. Epub 2018 Jan 18. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018. PMID: 29345179 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding institutional review boards: practical guidance to the IRB review process.Nutr Clin Pract. 2007 Dec;22(6):618-28. doi: 10.1177/0115426507022006618. Nutr Clin Pract. 2007. PMID: 18042949 Review.
-
Analysis of research ethics board approval times in an academic department of medicine.J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2015 Apr;10(2):145-50. doi: 10.1177/1556264615571557. Epub 2015 Feb 20. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2015. PMID: 25742673
-
Institutional Review Boards: What Clinician Researchers Need to Know.Mayo Clin Proc. 2019 Mar;94(3):515-525. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.01.020. Mayo Clin Proc. 2019. PMID: 30832791 Review.
Cited by
-
The Real-Time IRB: A Collaborative Innovation to Decrease IRB Review Time.J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018 Oct;13(4):432-437. doi: 10.1177/1556264618780803. Epub 2018 Jun 14. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018. PMID: 29902956 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory Support Improves Subsequent IRB Approval Rates in Studies Initially Deemed Not Ready for Review: A CTSA Institution's Experience.J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018 Apr;13(2):139-144. doi: 10.1177/1556264617752725. Epub 2018 Jan 18. J Empir Res Hum Res Ethics. 2018. PMID: 29345179 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating IACUCs: Previous Research and Future Directions.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2020 Nov 1;59(6):656-664. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-20-000077. Epub 2020 Sep 14. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32928341 Free PMC article.
-
Operational Characteristics of Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) in the United States.AJOB Empir Bioeth. 2019 Oct-Dec;10(4):276-286. doi: 10.1080/23294515.2019.1670276. Epub 2019 Oct 16. AJOB Empir Bioeth. 2019. PMID: 31618119 Free PMC article.
-
A snapshot of U.S. IRB review of COVID-19 research in the early pandemic.J Clin Transl Sci. 2021 Sep 13;5(1):e205. doi: 10.1017/cts.2021.848. eCollection 2021. J Clin Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 34956653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Check DK, Weinfurt KP, Dombeck CB, Kramer JM, Flynn KE. Use of central institutional review boards for multicenter clinical trials in the United States: a review of the literature. Clinical Trials. 2013;10:560–567. - PubMed
-
- Cleaton-Jones P. Process error rates in general research applications to the Human Research Ethics Committee (Medical) at the University of the Witwatersrand: a secondary data analysis. South African Journal of Bioethics & Law. 2010;3:20–24.
-
- Cleaton-Jones P. Applications and secretariat workload at the University of the Witwatersrand Human Research Ethics Committee (Medical) 2002-2011: a case study. South African Journal of Bioethics & Law. 2012;5:38–44.
-
- Clinical and Translational Science Awards Common Metrics Booklet. CTSA Program Annual Principal Investigator Meeting; Dec 16-17, 2015; Washington DC. 2015. Retrieved from https://ctsacentral.org/wp-content/uploads/CTSA-Common-Metrics-Booklet-1....
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

