Mechanics of ultrasound elastography
- PMID: 28413350
- PMCID: PMC5378248
- DOI: 10.1098/rspa.2016.0841
Mechanics of ultrasound elastography
Abstract
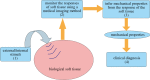
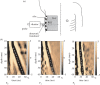
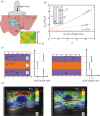
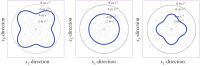
Ultrasound elastography enables in vivo measurement of the mechanical properties of living soft tissues in a non-destructive and non-invasive manner and has attracted considerable interest for clinical use in recent years. Continuum mechanics plays an essential role in understanding and improving ultrasound-based elastography methods and is the main focus of this review. In particular, the mechanics theories involved in both static and dynamic elastography methods are surveyed. They may help understand the challenges in and opportunities for the practical applications of various ultrasound elastography methods to characterize the linear elastic, viscoelastic, anisotropic elastic and hyperelastic properties of both bulk and thin-walled soft materials, especially the in vivo characterization of biological soft tissues.
Keywords: shear wave; soft tissues; ultrasound elastography.
Figures













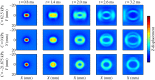
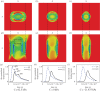




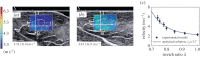

References
-
- Gao L, Parker KJ, Lerner RM, Levinson SF. 1996. Imaging of the elastic properties of tissue—a review. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 22, 959–977. (doi:10.1016/S0301-5629(96)00120-2) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ophir J, Alam SK, Garra B, Kallel F, Konofagou E, Krouskop T, Varghese T. 1999. Elastography: ultrasonic estimation and imaging of the elastic properties of tissues. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. H 213, 203–233. (doi:10.1243/0954411991534933) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Greenleaf JF, Fatemi M, Insana M. 2003. Selected methods for imaging elastic properties of biological tissues. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 5, 57–78. (doi:10.1146/annurev.bioeng.5.040202.121623) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sarvazyan A, Hall TJ, Urban MW, Fatemi M, Aglyamov SR, Garra BS. 2011. An overview of elastography – an emerging branch of medical imaging. Curr. Med. Imaging Rev. 7, 255–282. (doi:10.2174/157340511798038684) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Parker KJ, Doyley MM, Rubens DJ. 2011. Imaging the elastic properties of tissue: the 20 year perspective. Phys. Med. Biol. 56, R1 (doi:10.1088/0031-9155/56/1/R01) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
