Identification of miRNA biomarkers of pneumonia using RNA-sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
- PMID: 28413462
- PMCID: PMC5377245
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4151
Identification of miRNA biomarkers of pneumonia using RNA-sequencing and bioinformatics analysis
Abstract
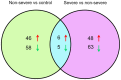
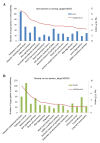
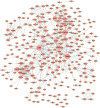
Pneumonia is a lower respiratory tract infection that causes dramatic mortality worldwide. The present study aimed to investigate the pathogenesis of pneumonia and identify microRNA (miRNA) biomarkers as candidates for targeted therapy. RNA from the peripheral blood plasma of participants with pneumonia (severe, n=9; non-severe, n=9) and controls (n=9) was isolated and paired-end sequencing was performed on an Illumina HiSeq4000 system. Following the processing of raw reads, the sequences were aligned against the Genome Reference Consortium human genome assembly 38 reference genome using Bowtie2 software. Reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped read values were obtained and the limma software package was used to identify differentially expressed miRNAs (DE-miRs). Then, DE-miR targets were predicted and subjected to enrichment analysis. In addition, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of the predicted targets was constructed. This analysis identified 11 key DE-miRs in pneumonia samples, including 6 upregulated miRNAs (including hsa-miR-34a and hsa-miR-455) and 5 downregulated miRNAs (including hsa-let-7f-1). All DE-miRs kept their upregulation/downregulation pattern in the control, non-severe pneumonia and severe pneumonia samples. Predicted target genes of DE-miRs in the subjects with non-severe pneumonia vs. the control and the subjects with severe pneumonia vs. the non-severe pneumonia group were markedly enriched in the adherens junction and Wnt signaling pathways. KALRN, Ras homolog family member A (RHOA), β-catenin (CTNNB1), RNA polymerase II subunit K (POLR2K) and amyloid precursor protein (APP) were determined to encode crucial proteins in the PPI network constructed. KALRN was predicted to be a target of hsa-mir-200b, while RHOA, CTNNB1, POLR2K and APP were predicted targets of hsa-let-7f-1. The results of the present study demonstrated that hsa-let-7f-1 may serve a role in the development of cancer and the Notch signaling pathway. Conversely, hsa-miR-455 may be an inhibitor of pneumonia pathogenesis. Furthermore, hsa-miR-200b might promote pneumonia via targeting KALRN.
Keywords: RNA-sequencing; miRNA; notch signaling pathway; pneumonia; protein-protein interaction; target.
Figures



Similar articles
-
miRNA signature identification of retinoblastoma and the correlations between differentially expressed miRNAs during retinoblastoma progression.Mol Vis. 2015 Dec 14;21:1307-17. eCollection 2015. Mol Vis. 2015. PMID: 26730174 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of biomarkers and construction of a microRNA-mRNA regulatory network for ependymoma using integrated bioinformatics analysis.Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):6079-6089. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10941. Epub 2019 Sep 30. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31788082 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Key Biomarkers and Therapeutic Drugs in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Through Pathway Enrichment Analysis and Hub Gene-miRNA Networks.Iran J Pharm Res. 2023 Nov 20;22(1):e139985. doi: 10.5812/ijpr-139985. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Iran J Pharm Res. 2023. PMID: 38444712 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-seq analysis of human vertebrae provides insight into the mechanism underlying GIOP.Bone. 2019 Mar;120:371-386. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.11.013. Epub 2018 Nov 29. Bone. 2019. PMID: 30503955
-
miRNA profiling of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines HONE1 and CNE2 after X-ray therapy.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2022 Jun;31(6):671-687. doi: 10.17219/acem/146580. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2022. PMID: 35275451
Cited by
-
Epigenetic interaction of microbes with their mammalian hosts.J Biosci. 2021;46(4):94. doi: 10.1007/s12038-021-00215-w. J Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34728591 Free PMC article.
-
B2M is a Biomarker Associated With Immune Infiltration In High Altitude Pulmonary Edema.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024;27(1):168-185. doi: 10.2174/1386207326666230510095840. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2024. PMID: 37165489 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-4485 ameliorates severe influenza pneumonia via inhibition of the STAT3/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.Oncol Lett. 2020 Nov;20(5):215. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12078. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32963621 Free PMC article.
-
let7f‑5p attenuates inflammatory injury in in vitro pneumonia models by targeting MAPK6.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Feb;23(2):95. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11734. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33300070 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical value of miR-200b in diagnosis and prognosis of childhood pneumonia.BMC Pediatr. 2025 Jan 18;25(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12887-024-05370-1. BMC Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 39825267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WH. whoint/mediacentre/factsheets/fs310/en. The top 10 causes of death. 2013 2014 Jul;
-
- Said MA, Johnson HL, Nonyane BA, Deloria-Knoll M, O'Brien KL, AGEDD Adult Pneumococcal Burden Study Team. Andreo F, Beovic B, Blanco S, Boersma WG, et al. Estimating the burden of pneumococcal pneumonia among adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic techniques. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060273. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
