The effects of GLP-1 analogues on pre-diabetes of the children
- PMID: 28413488
- PMCID: PMC5377282
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4129
The effects of GLP-1 analogues on pre-diabetes of the children
Abstract
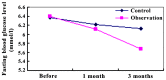
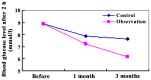
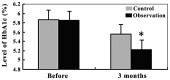
The aim of the study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues in children of pre-diabetes to delay or reverse the development of pre-diabetes into the state of diabetes by early intervention. Prospective and randomized controlled clinical trials were performed in 42 cases of newly diagnosed pre-diabetes in children. The sample size was randomly divided into the two groups. The first group included 21 subjects comprising the lifestyle intervention group, i.e., control group, and the second group included 21 subjects comprising the lifestyle intervention+GLP-1 analogues liraglutide group, i.e., observation group. Interventions carried out lasted 3 months. A review of intervention was carried out at 1 month and after 3 months. Medical examinations were carried out at the the time following diagnosis with pre-diabetes and after the intervention of 3 months. The medical test examinations included the fasting blood glucose (FPG), 2-hour postprandial blood glucose (2hPG), detection of glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1C), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), body mass index (BMI), insulin resistance (IR) and the islet cell functions. After 1 month of intervention, the observation group exhibited a better control on FPG and 2hPG compared with the control group (P<0.05). After 3 months of the intervention, FPG and 2hPG levels of the observation group were significantly lower than those of the control group (P<0.01). The levels of HbA1C, TC, TG, LDL-C, HDL-C, and BMI of the observation group were statistically better controlled, when compared with the control group after the intervention of 3 months. The IR index of the observation group was significantly decreased compared to that of the control group (P<0.05) and the islet function index of the β-cell of the observation group showed statistically higher values than that of the control group (P<0.05). In conclusion, GLP-1 analogues are a better regulator of blood sugar levels, effectively improve lipid profile, body mass, IR and islet β-cell function. Furthermore, GLP-1 analogues opens up a new way to intervene pre-diabetes in children.
Keywords: GLP-1 analogues; children; liraglutide; pre-diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP3) in serum of patients with gestational diabetes mellitus and its relationship with insulin resistance.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Dec;21(24):5702-5710. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201712_14016. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29272006
-
[The changes of gastrointestinal hormones GLP-1, PYY and ghrelin in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 Sep;44(5):774-8. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 24325110 Chinese.
-
[Relations between serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein and type 2 diabetes in a community population].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011 Mar;31(3):508-11. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2011. PMID: 21421494 Chinese.
-
Evaluation of the Clinical Efficacy of the Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by the Telemedicine Management System Based on the Internet of Things Technology.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jun 22;2022:8149515. doi: 10.1155/2022/8149515. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35785080 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Type 2 Diabetes in Youth.Glob Pediatr Health. 2021 May 6;7:2333794X20981343. doi: 10.1177/2333794X20981343. eCollection 2020. Glob Pediatr Health. 2021. PMID: 34036121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liraglutide suppresses obesity and promotes browning of white fat via miR-27b in vivo and in vitro.J Int Med Res. 2021 Nov;49(11):3000605211055059. doi: 10.1177/03000605211055059. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34772311 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on prediabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Jun 14;16(1):129. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01371-3. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 38877565 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of liraglutide for weight management in children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Nov;182(11):5095-5108. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05186-8. Epub 2023 Sep 6. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37672063
-
Consensus Recommendations on GLP-1 RA Use in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: South Asian Task Force.Diabetes Ther. 2019 Oct;10(5):1645-1717. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-0669-4. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Diabetes Ther. 2019. PMID: 31359367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Liraglutide for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in children and adolescents: has a new era arrived?Prz Gastroenterol. 2019;14(3):221-222. doi: 10.5114/pg.2019.88172. Epub 2019 Sep 27. Prz Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31649796 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous