Dramatic intracranial response to osimertinib in a poor performance status patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation: A case report
- PMID: 28413660
- PMCID: PMC5374897
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2017.1181
Dramatic intracranial response to osimertinib in a poor performance status patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation: A case report
Abstract
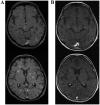
We herein report a case of dramatic intracranial response to osimertinib in a poor performance status patient with lung adenocarcinoma harboring the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M mutation encoded in exon 20. The patient was a 59-year-old woman with EGFR exon 19 deletion-positive lung adenocarcinoma, who relapsed with multiple brain metastases. Computed tomography-guided biopsy of the left pleural tumor revealed adenocarcinoma harboring an EGFR exon 19 deletion and an EGFR T790M mutation encoded in exon 20. The patient was treated with osimertinib, a third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Two days after treatment initiation, the patient displayed profound disturbance of consciousness, possibly due to carcinomatous meningitis, and treatment had to be discontinued due to difficulty in taking osimertinib. However, the patient gradually started to recover consciousness and, after 3 days, she was again able to take osimertinib. One month after the initiation of osimertinib treatment, magnetic resonance imaging revealed an apparent reduction in brain metastases. The patient is currently under continued treatment with osimertinib. At the last follow-up (February, 2017) she exhibited partial response to the treatment.
Keywords: brain metastasis; epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor; leptomeningeal carcinomatosis; osimertinib; poor performance status.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Treatment response to osimertinib in a patient with leptomeningeal metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma following failure of gefitinib and erlotinib: A case report.Mol Clin Oncol. 2018 Sep;9(3):321-324. doi: 10.3892/mco.2018.1666. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Mol Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30112177 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of osimertinib in a patient with non-small cell lung cancer harboring epithelial growth factor receptor exon 19 deletion/T790M mutation, with poor performance status.Mol Clin Oncol. 2018 Feb;8(2):246-249. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1522. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Mol Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29399354 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of osimertinib treatment on lung adenocarcinoma with squamous cell transformation harboring the T790M mutation: A case report and literature review.Mol Clin Oncol. 2019 Aug;11(2):127-131. doi: 10.3892/mco.2019.1880. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Mol Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31316771 Free PMC article.
-
A consensus on the role of osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer from the AME Lung Cancer Collaborative Group.J Thorac Dis. 2018 Jul;10(7):3909-3921. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2018.07.61. J Thorac Dis. 2018. PMID: 30174832 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in epidermal growth factor receptor -mutant non-small cell lung cancer.Lung Cancer. 2016 Mar;93:59-68. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2016.01.003. Epub 2016 Jan 8. Lung Cancer. 2016. PMID: 26898616 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of osimertinib against EGFRvIII+ glioblastoma.Oncotarget. 2020 Jun 2;11(22):2074-2082. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.27599. eCollection 2020 Jun 2. Oncotarget. 2020. PMID: 32547705 Free PMC article.
-
Osimertinib in Patients With Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Mutation-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Leptomeningeal Metastases: The BLOOM Study.J Clin Oncol. 2020 Feb 20;38(6):538-547. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00457. Epub 2019 Dec 6. J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 31809241 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment response to osimertinib in a patient with leptomeningeal metastasis from lung adenocarcinoma following failure of gefitinib and erlotinib: A case report.Mol Clin Oncol. 2018 Sep;9(3):321-324. doi: 10.3892/mco.2018.1666. Epub 2018 Jul 5. Mol Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 30112177 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Central Nervous System Metastases from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Oncologist. 2018 Oct;23(10):1199-1209. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0572. Epub 2018 Apr 12. Oncologist. 2018. PMID: 29650684 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of osimertinib in a patient with non-small cell lung cancer harboring epithelial growth factor receptor exon 19 deletion/T790M mutation, with poor performance status.Mol Clin Oncol. 2018 Feb;8(2):246-249. doi: 10.3892/mco.2017.1522. Epub 2017 Nov 29. Mol Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29399354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Usui K, Maemondo M, Okinaga S, Mikami I, Ando M, Yamazaki K, Saijo Y, Gemma A, et al. North East Japan Gefitinib Study Group First-line gefitinib for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harboring epidermal growth factor receptor mutations without indication for chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1394–1400. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.7658. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu HA, Arcila ME, Rekhtman N, Sima CS, Zakowski MF, Pao W, Kris MG, Miller VA, Ladanyi M, Riely GJ. Analysis of tumor specimens at the time of acquired resistance to EGFR-TKI therapy in 155 patients with EGFR-mutant lung cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:2240–2247. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2246. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous