Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis in a patient with extensive disease small-cell lung cancer
- PMID: 28413671
- PMCID: PMC5374934
- DOI: 10.3892/mco.2017.1162
Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis in a patient with extensive disease small-cell lung cancer
Abstract
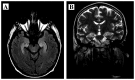
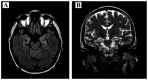
Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis (PLE) is a rare disorder infrequently accompanying malignancy, coexisting in ~50% of the cases with small-cell lung cancer (SCLC). The pathomechanism of PLE is considered to be immune-mediated, with production of specific anti-Hu antibodies and activation of T-cells directed against onconeural antigens present on both tumor cells and neurons. We herein report the case of a 50-year-old male patient who, prior to being diagnosed with SCLC, presented with typical symptoms of PLE (seizures, subacute cognitive dysfunction with severe memory impairment, anxiety and hallucinations). The initial brain magnetic resonance imaging examination revealed mild enlargement and hyperintensity of the hippocampal gyri bilaterally, with narrowed temporal horns of the lateral ventricles; the findings of the cerebrospinal fluid examination were compatible with the diagnosis of lymphocytic meningitis. Due to the suspected infectious origin of the disease, treatment with acyclovir and antibiotics was initially applied. However, following subsequent diagnosis of the underlying SCLC and the presence of antineuronal anti-Hu antibodies in the patient's serum, the diagnosis of PLE accompanying extensive-disease (ED) SCLC was confirmed. In addition to the standard cytotoxic therapy, throughout the course of his disease the patient also continued treatment with valproic acid (VPA) as prophylaxis for the initial seizures. VPA is known to be a potent histone deacetylase inhibitor that may reverse epigenetic changes in tumor cells and potentially improve the outcome of cancer patients. The patient succumbed to the disease 25 months after the diagnosis of malignancy; such a long course is observed in only ~5% of patients with ED SCLC. Therefore, it was hypothesized that the accompanying paraneoplasia and treatment with VPA may have improved the outcome in this patient.
Keywords: anti-Hu antibodies; chemotherapy; paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis; small-cell lung cancer; synergistic effect; valproic acid.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis: neurological symptoms, immunological findings and tumour association in 50 patients.Brain. 2000 Jul;123 ( Pt 7):1481-94. doi: 10.1093/brain/123.7.1481. Brain. 2000. PMID: 10869059 Clinical Trial.
-
Coexistence of anti-SOX1 and anti-GABAB receptor antibodies with paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis presenting with seizures and memory impairment in small cell lung cancer: A case report.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 28;13:955170. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955170. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35967304 Free PMC article.
-
"Limbic encephalitis with acute onset and Hu antibodies treated with rituximab: Paraneoplastic or non-paraneoplastic disorder?".Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019 Sep;184:105424. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2019.105424. Epub 2019 Jul 12. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31330415
-
[Limbic encephalitis with antibodies against intracellular antigens].Brain Nerve. 2010 Apr;62(4):347-55. Brain Nerve. 2010. PMID: 20420174 Review. Japanese.
-
[Limbic encephalitis: a probably under-recognized syndrome].Neurologia. 2005 Jan-Feb;20(1):24-30. Neurologia. 2005. PMID: 15704018 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes of small cell lung cancer.Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2024 Jun;33(2):80-92. doi: 10.5114/ppn.2024.141157. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Postep Psychiatr Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39119541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Neuropsychiatric Prelude to Unveiling Small Cell Lung Cancer with Suspected Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis: A Case Report.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jun 19;32(6):366. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32060366. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40558309 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
