In vivo reprogramming of immune cells: Technologies for induction of antigen-specific tolerance
- PMID: 28414079
- PMCID: PMC5582017
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2017.04.005
In vivo reprogramming of immune cells: Technologies for induction of antigen-specific tolerance
Abstract
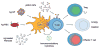
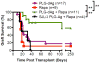
Technologies that induce antigen-specific immune tolerance by mimicking naturally occurring mechanisms have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of many immune-mediated pathologies such as autoimmunity, allograft rejection, and allergy. The immune system intrinsically has central and peripheral tolerance pathways for eliminating or modulating antigen-specific responses, which are being exploited through emerging technologies. Antigen-specific tolerogenic responses have been achieved through the functional reprogramming of antigen-presenting cells or lymphocytes. Alternatively, immune privileged sites have been mimicked using biomaterial scaffolds to locally suppress immune responses and promote long-term allograft survival. This review describes natural mechanisms of peripheral tolerance induction and the various technologies being developed to achieve antigen-specific immune tolerance in vivo. As currently approved therapies are non-specific and carry significant associated risks, these therapies offer significant progress towards replacing systemic immune suppression with antigen-specific therapies to curb aberrant immune responses.
Keywords: Allergy; Autoimmune disease; Drug delivery; Immune tolerance; Nanoparticle; Regulatory T cells; Transplantation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

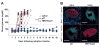
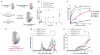


References
-
- Parish IA, Heath WR. Too dangerous to ignore: self-tolerance and the control of ignorant autoreactive T cells. Immunology and Cell Biology. 2008;86:146–152. - PubMed
-
- Miller SD, Turley DM, Podojil JR. Antigen-specific tolerance strategies for the prevention and treatment of autoimmune disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:665–677. - PubMed
-
- Peleg AY, Husain S, Kwak EJ, Silveira FP, Ndirangu M, Tran J, Shutt KA, Shapiro R, Thai N, Abu-Elmagd K. Opportunistic infections in 547 organ transplant recipients receiving alemtuzumab, a humanized monoclonal CD-52 antibody. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44:204–212. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

