Zseq: An Approach for Preprocessing Next-Generation Sequencing Data
- PMID: 28414515
- PMCID: PMC5563921
- DOI: 10.1089/cmb.2017.0021
Zseq: An Approach for Preprocessing Next-Generation Sequencing Data
Abstract
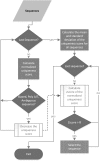
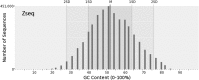
Next-generation sequencing technology generates a huge number of reads (short sequences), which contain a vast amount of genomic data. The sequencing process, however, comes with artifacts. Preprocessing of sequences is mandatory for further downstream analysis. We present Zseq, a linear method that identifies the most informative genomic sequences and reduces the number of biased sequences, sequence duplications, and ambiguous nucleotides. Zseq finds the complexity of the sequences by counting the number of unique k-mers in each sequence as its corresponding score and also takes into the account other factors such as ambiguous nucleotides or high GC-content percentage in k-mers. Based on a z-score threshold, Zseq sweeps through the sequences again and filters those with a z-score less than the user-defined threshold. Zseq algorithm is able to provide a better mapping rate; it reduces the number of ambiguous bases significantly in comparison with other methods. Evaluation of the filtered reads has been conducted by aligning the reads and assembling the transcripts using the reference genome as well as de novo assembly. The assembled transcripts show a better discriminative ability to separate cancer and normal samples in comparison with another state-of-the-art method. Moreover, de novo assembled transcripts from the reads filtered by Zseq have longer genomic sequences than other tested methods. Estimating the threshold of the cutoff point is introduced using labeling rules with optimistic results.
Keywords: RNA-SEQ analysis; machine learning; next-generation sequencing; preprocessing.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation and Validation of Assembling Corrected PacBio Long Reads for Microbial Genome Completion via Hybrid Approaches.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 7;10(12):e0144305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144305. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26641475 Free PMC article.
-
RAMBO-K: Rapid and Sensitive Removal of Background Sequences from Next Generation Sequencing Data.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 17;10(9):e0137896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137896. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26379285 Free PMC article.
-
SeqAssist: a novel toolkit for preliminary analysis of next-generation sequencing data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2014;15 Suppl 11(Suppl 11):S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-15-S11-S10. Epub 2014 Oct 21. BMC Bioinformatics. 2014. PMID: 25349885 Free PMC article.
-
The present and future of de novo whole-genome assembly.Brief Bioinform. 2018 Jan 1;19(1):23-40. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw096. Brief Bioinform. 2018. PMID: 27742661 Review.
-
The bioinformatics tools for the genome assembly and analysis based on third-generation sequencing.Brief Funct Genomics. 2019 Feb 14;18(1):1-12. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/ely037. Brief Funct Genomics. 2019. PMID: 30462154 Review.
Cited by
-
Generative Adversarial Networks for Creating Synthetic Nucleic Acid Sequences of Cat Genome.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 28;23(7):3701. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073701. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409058 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison of methods for multiple degree of freedom testing in repeated measures RNA-sequencing experiments.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022 May 28;22(1):153. doi: 10.1186/s12874-022-01615-8. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2022. PMID: 35643435 Free PMC article.
-
Music of metagenomics-a review of its applications, analysis pipeline, and associated tools.Funct Integr Genomics. 2022 Feb;22(1):3-26. doi: 10.1007/s10142-021-00810-y. Epub 2021 Oct 18. Funct Integr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 34657989 Review.
-
Transcriptomics Signature from Next-Generation Sequencing Data Reveals New Transcriptomic Biomarkers Related to Prostate Cancer.Cancer Inform. 2019 Mar 13;18:1176935119835522. doi: 10.1177/1176935119835522. eCollection 2019. Cancer Inform. 2019. PMID: 30890858 Free PMC article.
-
Benchmarking of Nanopore R10.4 and R9.4.1 flow cells in single-cell whole-genome amplification and whole-genome shotgun sequencing.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023 Mar 24;21:2352-2364. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2023.03.038. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2023. PMID: 37025654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown T. Introduction to Genetics: A Molecular Approach. Garland Science, 2012. ISBN 9780815365099. Available at: URL http://books.google.ca/books?id=TsvKPQAACAAJ Last viewed on Jan. 20, 2017
-
- Cortes C., and Vapnik V. 1995. Support-vector networks. Machine Learn. 20, 273–297
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
