Active transforming growth factor-β2 in the aqueous humor of posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy patients
- PMID: 28414732
- PMCID: PMC5393593
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175509
Active transforming growth factor-β2 in the aqueous humor of posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy patients
Abstract
Purpose: Posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy (PPCD) is characterized by abnormal proliferation of corneal endothelial cells. It was shown that TGF-β2 present in aqueous humor (AH) could help maintaining the corneal endothelium in a G1-phase-arrest state. We wanted to determine whether the levels of this protein are changed in AH of PPCD patients.
Methods: We determined the concentrations of active TGF-β2 in the AH of 29 PPCD patients (42 samples) and 40 cadaver controls (44 samples) by ELISA. For data analysis the PPCD patients were divided based on either the molecular genetic cause of their disease as PPCD1 (37 samples), PPCD3 (1 sample) and PPCDx (not linked to a known PPCD loci, 4 samples) or on the presence (17 samples) or absence (25 samples) of secondary glaucoma or on whether they had undergone penetrating keratoplasty (PK, 32 samples) or repeated PK (rePK, 7 samples).
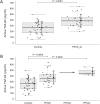
Results: The level of active TGF-β2 in the AH of all PPCD patients (mean ± SD; 386.98 ± 114.88 pg/ml) in comparison to the control group (260.95 ± 112.43 pg/ml) was significantly higher (P = 0.0001). Compared to the control group, a significantly higher level of active TGF-β2 was found in the PPCD1 (P = 0.0005) and PPCDx (P = 0.0022) groups. Among patients the levels of active TGF-β2 were not significantly affected by gender, age, secondary glaucoma or by the progression of dystrophy when one or repeated PK were performed.
Conclusion: The levels of active TGF-β2 in the AH of PPCD patients are significantly higher than control values, and thus the increased levels of TGF-β2 could be a consequence of the PPCD phenotype and can be considered as another feature characterizing this disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Determination of active TGF-beta2 in aqueous humor prior to and following cryopreservation.Mol Vis. 2006 Dec 2;12:1477-82. Mol Vis. 2006. PMID: 17167403
-
Alterations in GRHL2-OVOL2-ZEB1 axis and aberrant activation of Wnt signaling lead to altered gene transcription in posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy.Exp Eye Res. 2019 Nov;188:107696. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107696. Epub 2019 Jun 21. Exp Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31233731
-
Active transforming growth factor-beta2 is increased in the aqueous humor of keratoconus patients.Mol Vis. 2007 Jul 17;13:1198-202. Mol Vis. 2007. PMID: 17679942
-
[The pathogenesis and treatment of corneal disorders].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2002 Dec;106(12):757-76; discussion 777. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2002. PMID: 12610836 Review. Japanese.
-
[Research progress on proliferative property and capacity of human corneal endothelium].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011 Jan;40(1):94-100. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2011.01.017. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2011. PMID: 21319381 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
TGF-β-Mediated Modulation of Cell-Cell Interactions in Postconfluent Maturing Corneal Endothelial Cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022 Oct 3;63(11):3. doi: 10.1167/iovs.63.11.3. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2022. PMID: 36194422 Free PMC article.
-
PTEN Inhibition Accelerates Corneal Endothelial Wound Healing through Increased Endothelial Cell Division and Migration.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Jul 1;61(8):19. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.8.19. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32667999 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Merjava S, Liskova P, Sado Y, Davis PF, Greenhill NS, Jirsova K. Changes in the localization of collagens IV and VIII in corneas obtained from patients with posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy. Exp Eye Res. 2009;88(5):945–52. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.12.017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Davidson AE, Liskova P, Evans CJ, Dudakova L, Noskova L, Pontikos N, et al. Autosomal-Dominant Corneal Endothelial Dystrophies CHED1 and PPCD1 Are Allelic Disorders Caused by Non-coding Mutations in the Promoter of OVOL2. Am J Hum Genet. 2016;98(1):75–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2015.11.018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Biswas S, Munier FL, Yardley J, Hart-Holden N, Perveen R, Cousin P, et al. Missense mutations in COL8A2, the gene encoding the alpha2 chain of type VIII collagen, cause two forms of corneal endothelial dystrophy. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10(21):2415–23. - PubMed
-
- Krafchak CM, Pawar H, Moroi SE, Sugar A, Lichter PR, Mackey DA, et al. Mutations in TCF8 cause posterior polymorphous corneal dystrophy and ectopic expression of COL4A3 by corneal endothelial cells. Am J Hum Genet. 2005;77(5):694–708. doi: 10.1086/497348 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

