Tissue expression profiles and transcriptional regulation of elongase of very long chain fatty acid 6 in bovine mammary epithelial cells
- PMID: 28414811
- PMCID: PMC5393602
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175777
Tissue expression profiles and transcriptional regulation of elongase of very long chain fatty acid 6 in bovine mammary epithelial cells
Abstract
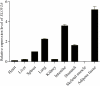
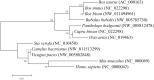
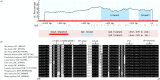
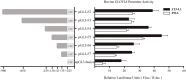
In mammals, very long chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) perform pleiotropic roles in a wide range of biological processes, such as cell membrane formation, cell signal transduction, and endocrine regulation. Beef and milk are abundant of palmitic acid which can be further elongated into stearic acid for synthesizing VLCFAs. Elongase of very long chain fatty acid 6 (ELOVL6) is a rate-limiting enzyme for converting palmitic acid to stearic acid. Consequently, investigating the tissue expression patterns and transcriptional regulation of bovine ELOVL6 can provide new insights into improving the composition of beneficial fats in cattle and expanding the knowledge of transcriptional regulation mechanism among domestic animals. In the current study, we found that bovine ELOVL6 expressed ubiquitously. Dual-luciferase reporter assay identified that the core promoter region (-130/-41 bp) was located in the second CpG island. In addition, the deletion mutation of binding sites demonstrated that sterol regulatory element binding transcription factor 1 (SREBF1) and specific protein 1 (SP1) both were able to stimulate bovine ELOVL6 promoter activity independently, while resulting the similar effect. To confirm these findings, further RNA interference assays were executed in bovine mammary epithelial cells (BMECs). In summary, these data suggest that bovine ELOVL6 expressed ubiquitously and is activated by SREBF1 and SP1, via two binding sites present in the ELOVL6 promoter region between -130 bp to -41bp.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fatty acid elongase7 is regulated via SP1 and is involved in lipid accumulation in bovine mammary epithelial cells.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun;233(6):4715-4725. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26255. Epub 2018 Jan 15. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29115671
-
ELOVL6 promoter binding sites directly targeted by sterol regulatory element binding protein 1 in fatty acid synthesis of goat mammary epithelial cells.J Dairy Sci. 2021 May;104(5):6253-6266. doi: 10.3168/jds.2020-19292. Epub 2021 Mar 6. J Dairy Sci. 2021. PMID: 33685712
-
Overexpression of SREBP1 (sterol regulatory element binding protein 1) promotes de novo fatty acid synthesis and triacylglycerol accumulation in goat mammary epithelial cells.J Dairy Sci. 2016 Jan;99(1):783-95. doi: 10.3168/jds.2015-9736. Epub 2015 Nov 18. J Dairy Sci. 2016. PMID: 26601584
-
[SREBP-1c and Elovl6 as Targets for Obesity-related Disorders].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2015;135(9):1003-9. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.15-00175-1. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 26329544 Review. Japanese.
-
[Role of Fatty Acid Elongase Elovl6 in the Regulation of Fatty Acid Quality and Lifestyle-related Diseases].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022;142(5):473-476. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.21-00176-4. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2022. PMID: 35491151 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Genomic insights into adaptation and inbreeding among Sub-Saharan African cattle from pastoral and agropastoral systems.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 25;15:1430291. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1430291. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39119582 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Cloning, Characterization, and Nutritional Regulation of Elovl6 in Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea).Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 11;20(7):1801. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071801. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30979053 Free PMC article.
-
Advances of Molecular Markers and Their Application for Body Variables and Carcass Traits in Qinchuan Cattle.Genes (Basel). 2019 Sep 17;10(9):717. doi: 10.3390/genes10090717. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31533236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The fatty acid elongase ELOVL6 regulates bortezomib resistance in multiple myeloma.Blood Adv. 2021 Apr 13;5(7):1933-1946. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020002578. Blood Adv. 2021. PMID: 33821992 Free PMC article.
-
Genome wide association study identifies SNPs associated with fatty acid composition in Chinese Wagyu cattle.J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2019 Mar 4;10:27. doi: 10.1186/s40104-019-0322-0. eCollection 2019. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30867906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hammad S, Pu S, Jones PJ. Current Evidence Supporting the Link Between Dietary Fatty Acids and Cardiovascular Disease. Lipids. 2016;51(5):507–17. Epub 2016/01/01. doi: 10.1007/s11745-015-4113-x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bazinet RP, Laye S. Polyunsaturated fatty acids and their metabolites in brain function and disease. Nature reviews Neuroscience. 2014;15(12):771–85. Epub 2014/11/13. doi: 10.1038/nrn3820 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Desvergne B, Michalik L, Wahli W. Transcriptional regulation of metabolism. Physiological reviews. 2006;86(2):465–514. Epub 2006/04/08. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00025.2005 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahmad Nizar NN, Nazrim Marikkar JM, Hashim DM. Differentiation of lard, chicken fat, beef fat and mutton fat by GCMS and EA-IRMS techniques. Journal of oleo science. 2013;62(7):459–64. Epub 2013/07/05. - PubMed
-
- Bonfatti V, Degano L, Menegoz A, Carnier P. Short communication: Mid-infrared spectroscopy prediction of fine milk composition and technological properties in Italian Simmental. Journal of dairy science. 2016;99(10):8216–21. Epub 2016/08/09. doi: 10.3168/jds.2016-10953 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

