Gallbladder papillary neoplasms share pathological features with intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct
- PMID: 28415560
- PMCID: PMC5458227
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16360
Gallbladder papillary neoplasms share pathological features with intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct
Abstract
Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct (IPNB) has been widely recognized. However, the knowledge of intracystic papillary neoplasm of the gallbladder (IPNG) including papillary adenoma and adenocarcinoma is not well defined. In this study, we compared the clinicopathological and immunohistochemical features between 32 IPNG cases and 32 IPNB cases. IPNG-1 (low-high grade dysplasia) exhibited an earlier onset age, smaller tumor size and lower level of CK20 expression compared to IPNG-2 (invasive carcinoma). Histologically, pancreaticobiliary and intestinal subtype accounted for nearly half of IPNG or IPNB (44.4% and 48.1% vs. 44.0% and 44.0%), respectively. Immunohistochemically, 88.9% of IPNG and 92.0% of IPNB cases were positive for MUC1, and 96.3% and 92.0% for CK7, respectively. CDX2 and MUC2 were more highly expressed in the intestinal subtype than in other subtypes. CK20 expression increased in parallel with tumor progression. In addition, 53.1% of IPNG cases and 68.6% of IPNB cases exhibited invasive carcinoma, and showed significant survival advantages to conventional gallbladder adenocarcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma, respectively. In conclusion, papillary adenoma and adenocarcinoma of the gallbladder can be recognized as different pathological stages of IPNG, and they share pathological features with IPNB.
Keywords: CDX2; cytokeratin; gallbladder; mucin; papillary.
Conflict of interest statement
There was no conflicts of interests to declare.
Figures

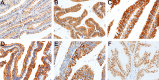


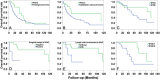
References
-
- Zen Y, Sasaki M, Fujii T, Chen TC, Chen MF, Yeh TS, Jan YY, Huang SF, Nimura Y, Nakanuma Y. Different expression patterns of mucin core proteins and cytokeratins during intrahepatic cholangiocarcinogenesis from biliary intraepithelial neoplasia and intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct—an immunohistochemical study of 110 cases of hepatolithiasis. Journal of hepatology. 2006;44:350–358. - PubMed
-
- Yeh TS, Tseng JH, Chen TC, Liu NJ, Chiu CT, Jan YY, Chen MF. Characterization of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma of the intraductal growth-type and its precursor lesions. Hepatology. 2005;42:657–664. - PubMed
-
- Rocha FG, Lee H, Katabi N, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y, D’Angelica MI, Allen PJ, Klimstra DS, Jarnagin WR. Intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct: a biliary equivalent to intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas? Hepatology. 2012;56:1352–1360. - PubMed
-
- Zen Y, Fujii T, Itatsu K, Nakamura K, Minato H, Kasashima S, Kurumaya H, Katayanagi K, Kawashima A, Masuda S, Niwa H, Mitsui T, Asada Y, et al. Biliary papillary tumors share pathological features with intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas. Hepatology. 2006;44:1333–1343. - PubMed
-
- Jung G, Park KM, Lee SS, Yu E, Hong SM, Kim J. Long-term clinical outcome of the surgically resected intraductal papillary neoplasm of the bile duct. Journal of hepatology. 2012;57:787–793. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

