IK channel activation increases tumor growth and induces differential behavioral responses in two breast epithelial cell lines
- PMID: 28415575
- PMCID: PMC5522074
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16389
IK channel activation increases tumor growth and induces differential behavioral responses in two breast epithelial cell lines
Abstract
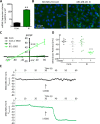
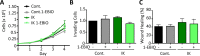
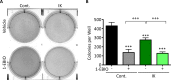
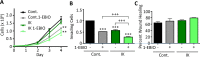
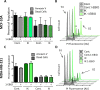
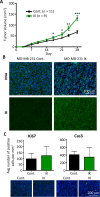
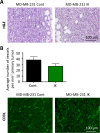
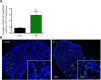
Many potassium channel families are over-expressed in cancer, but their mechanistic role in disease progression is poorly understood. Potassium channels modulate membrane potential (Vmem) and thereby influence calcium ion dynamics and other voltage-sensitive signaling mechanisms, potentially acting as transcriptional regulators. This study investigated the differential response to over-expression and activation of a cancer-associated potassium channel, the intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel (IK), on aggressive behaviors in mammary epithelial and breast cancer cell lines. IK was over-expressed in the highly metastatic breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 and the spontaneously immortalized breast epithelial cell line MCF-10A, and the effect on cancer-associated behaviors was assessed. IK over-expression increased primary tumor growth and metastasis of MDA-MB-231 in orthotopic xenografts, demonstrating for the first time in any cancer type that increased IK is sufficient to promote cancer aggression. The primary tumors had similar vascularization as determined by CD31 staining and similar histological characteristics. Interestingly, despite the increased in vivo growth and metastasis, neither IK over-expression nor activation with agonist had a significant effect on MDA-MB-231 proliferation, invasion, or migration in vitro. In contrast, IK decreased MCF-10A proliferation and invasion through Matrigel but had no effect on migration in a scratch-wound assay. We conclude that IK activity is sufficient to promote cell aggression in vivo. Our data provide novel evidence supporting IK and downstream signaling networks as potential targets for cancer therapies.
Keywords: bioelectricity; cancer; oncochannel; potassium channel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Ca2+-activated K+ channel of intermediate conductance: a molecular target for novel treatments?Curr Drug Targets. 2001 Dec;2(4):401-22. doi: 10.2174/1389450013348173. Curr Drug Targets. 2001. PMID: 11732639 Review.
-
Changes in the K+ current-density of MCF-7 cells during progression through the cell cycle: possible involvement of a h-ether.a-gogo K+ channel.Recept Channels. 2001;7(5):345-56. Recept Channels. 2001. PMID: 11697078
-
Investigation of the Effects of Blocking Potassium Channels With 4-Aminopyridine on Paclitaxel Activity in Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024 Dec;7(12):e70072. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70072. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 39648339 Free PMC article.
-
Role of KCNMA1 gene in breast cancer invasion and metastasis to brain.BMC Cancer. 2009 Jul 29;9:258. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-258. BMC Cancer. 2009. PMID: 19640305 Free PMC article.
-
The Ca2+-activated K+ channel of intermediate conductance:a possible target for immune suppression.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2002 Dec;6(6):623-36. doi: 10.1517/14728222.6.6.623. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2002. PMID: 12472376 Review.
Cited by
-
Electrical excitability of cancer cells-CELEX model updated.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Dec;43(4):1579-1591. doi: 10.1007/s10555-024-10195-6. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 38976181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Ion Channels for Cancer Treatment: Current Progress and Future Challenges.Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022;183:1-43. doi: 10.1007/112_2020_46. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 32865696 Review.
-
EDEn-Electroceutical Design Environment: Ion Channel Tissue Expression Database with Small Molecule Modulators.iScience. 2019 Jan 25;11:42-56. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2018.12.003. Epub 2018 Dec 11. iScience. 2019. PMID: 30590250 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Choreography and Structure of Ca2+ Release-Activated Ca2+ (CRAC) and KCa2+ Channels and Their Relevance in Disease with Special Focus on Cancer.Membranes (Basel). 2020 Dec 15;10(12):425. doi: 10.3390/membranes10120425. Membranes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33333945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KCNN4 as a genomic determinant of cytosolic delivery by the attenuated cationic lytic peptide L17E.Mol Ther. 2025 Feb 5;33(2):595-614. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.12.050. Epub 2025 Jan 1. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39748507
References
-
- Institute NC . National Cancer Institute; 2012. SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Female Breast Cancer. Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results Program.http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html
-
- Mina LA, Sledge GW., Jr Rethinking the metastatic cascade as a therapeutic target. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8:325–332. - PubMed
-
- Huber SM. Oncochannels. Cell calcium. 2013;53:241–255. - PubMed
-
- Cardone RA, Casavola V, Reshkin SJ. The role of disturbed pH dynamics and the Na+/H+ exchanger in metastasis. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2005;5:786–795. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

