A phase 2 study of vorinostat in locally advanced, recurrent, or metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma
- PMID: 28415633
- PMCID: PMC5464838
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16464
A phase 2 study of vorinostat in locally advanced, recurrent, or metastatic adenoid cystic carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: Vorinostat is a histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi). Based on a confirmed partial response (PR) in an adenoid cystic carcinoma (ACC) patient treated with vorinostat in a prior phase 1 trial, we initiated this phase 2 trial.
Methods: Vorinostat was administered orally 400 mg daily, 28 day cycles. The primary objective was to evaluate response rate (RR). Exploratory studies included whole exome sequencing (WES) of selected patients.
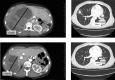
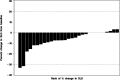
Results: Thirty patients were enrolled. Median age of patients was 53 years (range 21-73). Median number of cycles was 5 (range 1-66). Lymphopenia (n = 5), hypertension (n = 3), oral pain (n = 2), thromboembolic events (n = 2) and fatigue (n = 2) were the only grade 3 adverse events (AEs) that occurred in more than 1 patient. Eleven patients were dose reduced secondary to drug-related AEs. Two patients had a partial response (PR), with response durations of 53 and 7.2 months. One patient had a minor response with a decrease in ascites (for 19 cycles). Stable disease was the best response in 27 patients. Targeted and WES of 8 patients in this trial identified mutations in chromatin remodeling genes highlighting the role of the epigenome in ACC.
Conclusion: Vorinostat demonstrated efficacy in patients with ACC supporting the inclusion of HDACi in future studies to treat ACC.
Keywords: SAHA; adenoid cystic; salivary gland tumor; suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid; vorinostat.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors except LS and JC have no conflicts of interest. LS has research funding (for clinical trials) from Merck and is on Merck advisory board. JC has research funding (institutional for clinical trials) from Merck.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phase II study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid; SAHA) in recurrent or metastatic transitional cell carcinoma of the urothelium - an NCI-CTEP sponsored: California Cancer Consortium trial, NCI 6879.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Jun;39(3):812-820. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-01038-6. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33409898 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II trial of dasatinib for recurrent or metastatic c-KIT expressing adenoid cystic carcinoma and for nonadenoid cystic malignant salivary tumors.Ann Oncol. 2016 Feb;27(2):318-23. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdv537. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Ann Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26598548 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II trial of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat (Zolinza, suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, SAHA) in patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck cancer.Invest New Drugs. 2008 Feb;26(1):81-7. doi: 10.1007/s10637-007-9075-2. Epub 2007 Oct 25. Invest New Drugs. 2008. PMID: 17960324 Clinical Trial.
-
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors for Recurrent or Metastatic Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Jul 1;150(7):587-597. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2024.1177. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38814585 Free PMC article.
-
Salivary gland adenoid cystic carcinoma: a review of chemotherapy and molecular therapies.Oral Oncol. 2006 Sep;42(8):759-69. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2006.01.001. Epub 2006 Jun 6. Oral Oncol. 2006. PMID: 16757203 Review.
Cited by
-
The effectiveness of targeted therapy for recurrence or metastasis adenoid cystic carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ann Med. 2024 Dec;56(1):2399867. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2399867. Epub 2024 Sep 11. Ann Med. 2024. PMID: 39258959 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Histone Deacetylases in the Pathogenesis of Salivary Gland Tumors and Therapeutic Targeting Options.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 12;24(12):10038. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210038. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary Gland Carcinoma: Novel Targets to Overcome Treatment Resistance in Advanced Disease.Front Oncol. 2020 Oct 22;10:580141. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.580141. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33194707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective inhibition of cancer cell self-renewal through a Quisinostat-histone H1.0 axis.Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 14;11(1):1792. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15615-z. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32286289 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of MYB transcription factors in cancer drug resistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Apr 30;7:15. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2023.158. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 38835346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ellington CL, Goodman M, Kono SA, Grist W, Wadsworth T, Chen AY, Owonikoko T, Ramalingam S, Shin DM, Khuri FR, Beitler JJ, Saba NF. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck: Incidence and survival trends based on 1973–2007 Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results data. Cancer. 2012;118:4444–4451. - PubMed
-
- Spiro RH. Distant metastasis in adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary origin. American journal of surgery. 1997;174:495–498. - PubMed
-
- Ramalingam SS, Kummar S, Sarantopoulos J, Shibata S, LoRusso P, Yerk M, Holleran J, Lin Y, Beumer JH, Harvey RD, Ivy SP, Belani CP, Egorin MJ. Phase I study of vorinostat in patients with advanced solid tumors and hepatic dysfunction: a National Cancer Institute Organ Dysfunction Working Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2010;28:4507–4512. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

