Contrast agents in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 28415647
- PMCID: PMC5522164
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16482
Contrast agents in dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
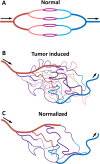
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (DCE-MRI) is a noninvasive method to assess angiogenesis, which is widely used in clinical applications including diagnosis, monitoring therapy response and prognosis estimation in cancer patients. Contrast agents play a crucial role in DCE-MRI and should be carefully selected in order to improve accuracy in DCE-MRI examination. Over the past decades, there was much progress in the development of optimal contrast agents in DCE-MRI. In this review, we describe the recent research advances in this field and discuss properties of contrast agents, as well as their advantages and disadvantages. Finally, we discuss the research perspectives for improving this promising imaging method.
Keywords: DCE-MRI; contrast agent; low molecular contrast agent; macromolecular contrast agent; nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for oncology drug development.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Aug;44(2):251-64. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25173. Epub 2016 Feb 8. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26854494 Review.
-
MR imaging of tumor microcirculation: promise for the new millennium.J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999 Dec;10(6):903-7. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1522-2586(199912)10:6<903::aid-jmri1>3.0.co;2-a. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1999. PMID: 10581502
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in oncology.Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2001 Aug;12(4):301-8. doi: 10.1097/00002142-200108000-00006. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2001. PMID: 11687716 Review.
-
Dynamic Contrast-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Diagnostic Tool in the Assessment of Tumour Angiogenesis in Urinary Bladder Cancer.Can Assoc Radiol J. 2019 Aug;70(3):254-263. doi: 10.1016/j.carj.2018.11.004. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Can Assoc Radiol J. 2019. PMID: 30922786
-
Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for assessing tumor vascularity and vascular effects of targeted therapies in renal cell carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2007 Jan 15;13(2 Pt 2):770s-776s. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1921. Clin Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17255308 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Value of Multimodal Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Discriminating Between Metastatic and Non-Metastatic Pelvic Lymph Nodes in Cervical Cancer.Int J Gen Med. 2022 Jul 22;15:6279-6288. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S372154. eCollection 2022. Int J Gen Med. 2022. PMID: 35911622 Free PMC article.
-
Saturation transfer properties of tumour xenografts derived from prostate cancer cell lines 22Rv1 and DU145.Sci Rep. 2020 Dec 4;10(1):21315. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-78353-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33277574 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive model based on DCE-MRI and clinical features for the evaluation of pain response after stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with spinal metastases.Eur Radiol. 2023 Jul;33(7):4812-4821. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-09437-y. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Eur Radiol. 2023. PMID: 36735042
-
Combination of DCE-MRI and DWI in Predicting the Treatment Effect of Concurrent Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 16;2020:2576563. doi: 10.1155/2020/2576563. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32626736 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Two Mathematical Models of Cellularity Calculation.Transl Oncol. 2018 Apr;11(2):307-310. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.01.020. Epub 2018 Feb 3. Transl Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29413764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farnsworth RH, Lackmann M, Achen MG, Stacker SA. Vascular remodeling in cancer. Oncogene. 2014;33:3496–505. - PubMed
-
- Armulik A, Genove G, Betsholtz C. Pericytes: developmental, physiological, and pathological perspectives, problems, and promises. Dev Cell. 2011;21:193–215. - PubMed
-
- Wong CI, Koh TS, Soo R, Hartono S, Thng CH, McKeegan E, Yong WP, Chen CS, Lee SC, Wong J, Lim R, Sukri N, Lim SE, et al. Phase I and biomarker study of ABT-869, a multiple receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in patients with refractory solid malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4718–26. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

