Diabetes mellitus and the risk of gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies
- PMID: 28415651
- PMCID: PMC5546528
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16487
Diabetes mellitus and the risk of gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies
Abstract
Studies examining the relationship between diabetes mellitus (DM) and the risk of gastric cancer incidence or gastric cancer mortality have produced inconsistent results. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the evidence regarding the relationship between DM and subsequent gastric cancer incidence or gastric cancer mortality risk on the basis of cohort studies. A systematic search of articles in PubMed, EmBase, the Cochrane Library, and reference lists was conducted to identify relevant literature. Twenty-two cohort studies reporting data on 8,559,861 participants were included in the study. Overall, participants with DM had little or no change in the risk of gastric cancer, or gastric cancer mortality. There was no evidence of difference in the RR for gastric cancer between men and women. Participants with DM had a non-significant trend towards an increased risk of gastric cancer mortality in men. There was no significant difference between men and women for this relationship. Finally, although subgroup analysis suggested DM was associated with a significant impact on gastric cancer incidence and gastric cancer mortality risk in several specific populations, a significance based on gender difference was not observed. In conclusion, DM might increase the risk of gastric cancer in men when the study used standard incidence/mortality ratio as effect estimate. Further, DM were associated with higher risk of gastric cancer mortality in men if the mean age at baseline less than 55.0 years, used RR or HR as effect estimate, the study adjusted smoking or not, and the study not adjusted alcohol drinking.
Keywords: diabetes mellitus; gastric cancer; gender; meta-analysis; prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures


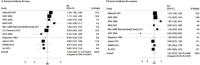


References
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H. Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1047–53. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National Diabetes Fact Sheet: National Estimates and General Information on Diabetes and Pre-diabetes in the United States. Atlanta: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2011. 2011.
-
- International Diabetes Federation Diabetes atlas. International Diabetes Federation. 2013.
-
- Palmer SC, Mavridis D, Navarese E, Craig JC, Tonelli M, Salanti G, Wiebe N, Ruospo M, Wheeler DC, Strippoli GF. Comparative efficacy and safety of blood pressure-lowering agents in adults with diabetes and kidney disease: a network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2015;385:2047–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

